Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies - NIHR Health ...
Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies - NIHR Health ...
Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies - NIHR Health ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
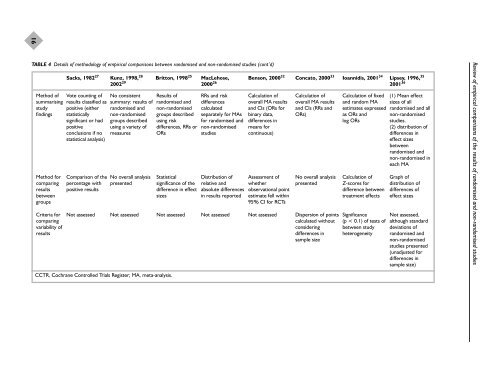
16TABLE 4 Details of methodology of empirical comparisons between <strong>randomised</strong> and <strong>non</strong>-<strong>randomised</strong> <strong>studies</strong> (cont’d)Method ofsummarisingstudyfindingsMethod forcomparingresultsbetweengroupsCriteria forcomparingvariability ofresultsSacks, 1982 27 Kunz, 1998, 28 Britton, 1998 25 MacLehose, Benson, 2000 32 Concato, 2000 33 Ioannidis, 2001 34 Lipsey, 1996, 352002 29 2000 26 2001 36Vote counting ofresults classified aspositive (eitherstatisticallysignificant or hadpositiveconclusions if nostatistical analysis)Comparison of thepercentage withpositive resultsNo consistentsummary: results of<strong>randomised</strong> and<strong>non</strong>-<strong>randomised</strong>groups describedusing a variety ofmeasuresNo overall analysispresentedResults of<strong>randomised</strong> and<strong>non</strong>-<strong>randomised</strong>groups describedusing riskdifferences, RRs orORsStatisticalsignificance of thedifference in effectsizesRRs and riskdifferencescalculatedseparately for MAsfor <strong>randomised</strong> and<strong>non</strong>-<strong>randomised</strong><strong>studies</strong>Distribution ofrelative andabsolute differencesin results reportedCalculation ofoverall MA resultsand CIs (ORs forbinary data,differences inmeans forcontinuous)Assessment ofwhetherobservational pointestimate fell within95% CI for RCTsCalculation ofoverall MA resultsand CIs (RRs andORs)No overall analysispresentedNot assessed Not assessed Not assessed Not assessed Not assessed Dispersion of pointscalculated withoutconsideringdifferences insample sizeCalculation of fixedand random MAestimates expressedas ORs andlog ORsCalculation ofZ-scores fordifference betweentreatment effectsSignificance(p < 0.1) of tests ofbetween studyheterogeneity(1) Mean effectsizes of all<strong>randomised</strong> and all<strong>non</strong>-<strong>randomised</strong><strong>studies</strong>.(2) distribution ofdifferences ineffect sizesbetween<strong>randomised</strong> and<strong>non</strong>-<strong>randomised</strong> ineach MAGraph ofdistribution ofdifferences ofeffect sizesNot assessed,although standarddeviations of<strong>randomised</strong> and<strong>non</strong>-<strong>randomised</strong><strong>studies</strong> presented(unadjusted fordifferences insample size)Review of empirical comparisons of the results of <strong>randomised</strong> and <strong>non</strong>-<strong>randomised</strong> <strong>studies</strong>CCTR, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register; MA, meta-analysis.