computer modeling in molecular biology.pdf
computer modeling in molecular biology.pdf
computer modeling in molecular biology.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
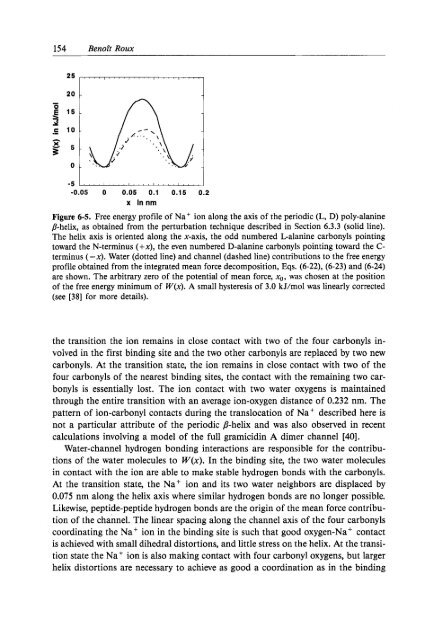
154 Benoft Roux-.3.-15-c 10 -h5 5 -30 --0.05 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2x <strong>in</strong>nmFigure 6-5. Free energy profile of Na' ion along the axis of the periodic (L, D) poly-alan<strong>in</strong>eP-helix, as obta<strong>in</strong>ed from the perturbation technique described <strong>in</strong> Section 6.3.3 (solid l<strong>in</strong>e).The helix axis is oriented along the x-axis, the odd numbered Lalan<strong>in</strong>e carbonyls po<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>gtoward the N-term<strong>in</strong>us (+x), the even numbered D-alan<strong>in</strong>e carbonyls po<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g toward the C-term<strong>in</strong>us (-x). Water (dotted l<strong>in</strong>e) and channel (dashed l<strong>in</strong>e) contributions to the free energyprofile obta<strong>in</strong>ed from the <strong>in</strong>tegrated mean force decomposition, Eqs. (6-22), (6-23) and (6-24)are shown. The arbitrary zero of the potential of mean force, xo, was chosen at the positionof the free energy m<strong>in</strong>imum of W(x). A small hysteresis of 3.0 kJ/mol was l<strong>in</strong>early corrected(see [38] for more details).the transition the ion rema<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong> close contact with two of the four carbonyls <strong>in</strong>volved<strong>in</strong> the first b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g site and the two other carbonyls are replaced by two newcarbonyls. At the transition state, the ion rema<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong> close contact with two of thefour carbonyls of the nearest b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g sites, the contact with the rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g two carbonylsis essentially lost. The ion contact with two water oxygens is ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>edthrough the entire transition with an average ion-oxygen distance of 0.232 nm. Thepattern of ion-carbonyl contacts dur<strong>in</strong>g the translocation of Na' described here isnot a particular attribute of the periodic P-helix and was also observed <strong>in</strong> recentcalculations <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g a model of the full gramicid<strong>in</strong> A dimer channel [40].Water-channel hydrogen bond<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>teractions are responsible for the contributionsof the water molecules to W(x). In the b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g site, the two water molecules<strong>in</strong> contact with the ion are able to make stable hydrogen bonds with the carbonyls.At the transition state, the Na' ion and its two water neighbors are displaced by0.075 nm along the helix axis where similar hydrogen bonds are no longer possible.Likewise, peptide-peptide hydrogen bonds are the orig<strong>in</strong> of the mean force contributionof the channel. The l<strong>in</strong>ear spac<strong>in</strong>g along the channel axis of the four carbonylscoord<strong>in</strong>at<strong>in</strong>g the Na' ion <strong>in</strong> the b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g site is such that good oxygen-Na' contactis achieved with small dihedral distortions, and little stress on the helix. At the transitionstate the Na+ ion is also mak<strong>in</strong>g contact with four carbonyl oxygens, but largerhelix distortions are necessary to achieve as good a coord<strong>in</strong>ation as <strong>in</strong> the b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g