Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older adults admitted to ...
Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older adults admitted to ...
Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older adults admitted to ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
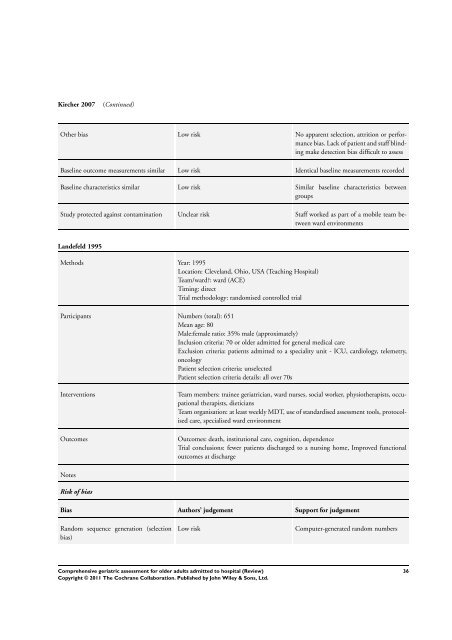
Kircher 2007 (Continued)<br />
Other bias Low risk No apparent selection, attrition or per<strong>for</strong>mance<br />
bias. Lack of patient and staff blinding<br />
make detection bias difficult <strong>to</strong> assess<br />
Baseline outcome measurements similar Low risk Identical baseline measurements recorded<br />
Baseline characteristics similar Low risk Similar baseline characteristics between<br />
groups<br />
Study protected against contamination Unclear risk Staff worked as part of a mobile team between<br />
ward environments<br />
Landefeld 1995<br />
Methods Year: 1995<br />
Location: Cleveland, Ohio, USA (Teaching Hospital)<br />
Team/ward?: ward (ACE)<br />
Timing: direct<br />
Trial methodology: randomised controlled trial<br />
Participants Numbers (<strong>to</strong>tal): 651<br />
Mean age: 80<br />
Male:female ratio: 35% male (approximately)<br />
Inclusion criteria: 70 or <strong>older</strong> <strong>admitted</strong> <strong>for</strong> general medical care<br />
Exclusion criteria: patients <strong>admitted</strong> <strong>to</strong> a speciality unit - ICU, cardiology, telemetry,<br />
oncology<br />
Patient selection criteria: unselected<br />
Patient selection criteria details: all over 70s<br />
Interventions Team members: trainee <strong>geriatric</strong>ian, ward nurses, social worker, physiotherapists, occupational<br />
therapists, dieticians<br />
Team organisation: at least weekly MDT, use of standardised <strong>assessment</strong> <strong>to</strong>ols, pro<strong>to</strong>colised<br />
care, specialised ward environment<br />
Outcomes Outcomes: death, institutional care, cognition, dependence<br />
Trial conclusions: fewer patients discharged <strong>to</strong> a nursing home, Improved functional<br />
outcomes at discharge<br />
Notes<br />
Risk of bias<br />
Bias Authors’ judgement Support <strong>for</strong> judgement<br />
Random sequence generation (selection<br />
bias)<br />
<strong>Comprehensive</strong> <strong>geriatric</strong> <strong>assessment</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>older</strong> <strong>adults</strong> <strong>admitted</strong> <strong>to</strong> hospital (Review)<br />
Copyright © 2011 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.<br />
Low risk Computer-generated random numbers<br />
36