Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older adults admitted to ...
Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older adults admitted to ...
Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older adults admitted to ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
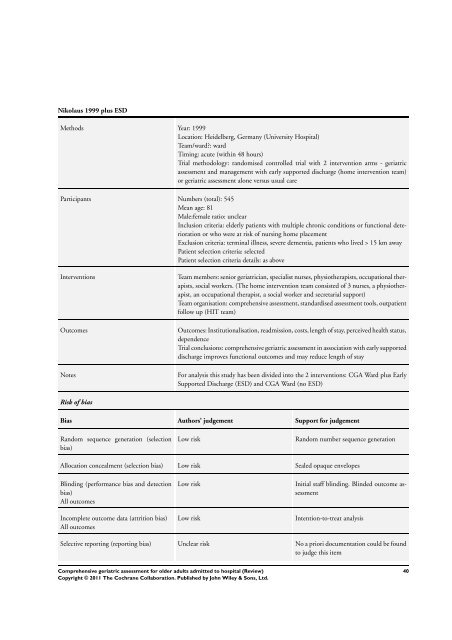
Nikolaus 1999 plus ESD<br />
Methods Year: 1999<br />
Location: Heidelberg, Germany (University Hospital)<br />
Team/ward?: ward<br />
Timing: acute (within 48 hours)<br />
Trial methodology: randomised controlled trial with 2 intervention arms - <strong>geriatric</strong><br />
<strong>assessment</strong> and management with early supported discharge (home intervention team)<br />
or <strong>geriatric</strong> <strong>assessment</strong> alone versus usual care<br />
Participants Numbers (<strong>to</strong>tal): 545<br />
Mean age: 81<br />
Male:female ratio: unclear<br />
Inclusion criteria: elderly patients with multiple chronic conditions or functional deterioration<br />
or who were at risk of nursing home placement<br />
Exclusion criteria: terminal illness, severe dementia, patients who lived > 15 km away<br />
Patient selection criteria: selected<br />
Patient selection criteria details: as above<br />
Interventions Team members: senior <strong>geriatric</strong>ian, specialist nurses, physiotherapists, occupational therapists,<br />
social workers. (The home intervention team consisted of 3 nurses, a physiotherapist,<br />
an occupational therapist, a social worker and secretarial support)<br />
Team organisation: comprehensive <strong>assessment</strong>, standardised <strong>assessment</strong> <strong>to</strong>ols, outpatient<br />
follow up (HIT team)<br />
Outcomes Outcomes: Institutionalisation, readmission, costs, length of stay, perceived health status,<br />
dependence<br />
Trial conclusions: comprehensive <strong>geriatric</strong> <strong>assessment</strong> in association with early supported<br />
discharge improves functional outcomes and may reduce length of stay<br />
Notes For analysis this study has been divided in<strong>to</strong> the 2 interventions: CGA Ward plus Early<br />
Supported Discharge (ESD) and CGA Ward (no ESD)<br />
Risk of bias<br />
Bias Authors’ judgement Support <strong>for</strong> judgement<br />
Random sequence generation (selection<br />
bias)<br />
Low risk Random number sequence generation<br />
Allocation concealment (selection bias) Low risk Sealed opaque envelopes<br />
Blinding (per<strong>for</strong>mance bias and detection<br />
bias)<br />
All outcomes<br />
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias)<br />
All outcomes<br />
Low risk Initial staff blinding. Blinded outcome <strong>assessment</strong><br />
Low risk Intention-<strong>to</strong>-treat analysis<br />
Selective reporting (reporting bias) Unclear risk No a priori documentation could be found<br />
<strong>to</strong> judge this item<br />
<strong>Comprehensive</strong> <strong>geriatric</strong> <strong>assessment</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>older</strong> <strong>adults</strong> <strong>admitted</strong> <strong>to</strong> hospital (Review)<br />
Copyright © 2011 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.<br />
40