MAXIMIZING POSITIVE SYNERGIES - World Health Organization
MAXIMIZING POSITIVE SYNERGIES - World Health Organization
MAXIMIZING POSITIVE SYNERGIES - World Health Organization
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
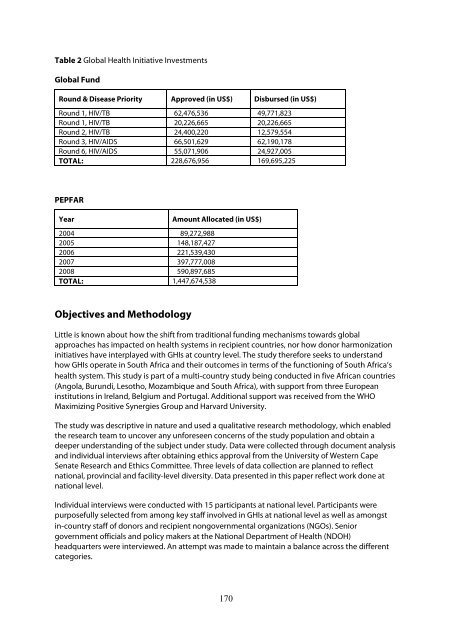
Table 2 Global <strong>Health</strong> Initiative Investments<br />
Global Fund<br />
Round & Disease Priority Approved (in US$) Disbursed (in US$)<br />
Round 1, HIV/TB 62,476,536 49,771,823<br />
Round 1, HIV/TB 20,226,665 20,226,665<br />
Round 2, HIV/TB 24,400,220 12,579,554<br />
Round 3, HIV/AIDS 66,501,629 62,190,178<br />
Round 6, HIV/AIDS 55,071,906 24,927,005<br />
TOTAL: 228,676,956 169,695,225<br />
PEPFAR<br />
Year Amount Allocated (in US$)<br />
2004 89,272,988<br />
2005 148,187,427<br />
2006 221,539,430<br />
2007 397,777,008<br />
2008 590,897,685<br />
TOTAL: 1,447,674,538<br />
Objectives and Methodology<br />
Little is known about how the shift from traditional funding mechanisms towards global<br />
approaches has impacted on health systems in recipient countries, nor how donor harmonization<br />
initiatives have interplayed with GHIs at country level. The study therefore seeks to understand<br />
how GHIs operate in South Africa and their outcomes in terms of the functioning of South Africa’s<br />
health system. This study is part of a multi‐country study being conducted in five African countries<br />
(Angola, Burundi, Lesotho, Mozambique and South Africa), with support from three European<br />
institutions in Ireland, Belgium and Portugal. Additional support was received from the WHO<br />
Maximizing Positive Synergies Group and Harvard University.<br />
The study was descriptive in nature and used a qualitative research methodology, which enabled<br />
the research team to uncover any unforeseen concerns of the study population and obtain a<br />
deeper understanding of the subject under study. Data were collected through document analysis<br />
and individual interviews after obtaining ethics approval from the University of Western Cape<br />
Senate Research and Ethics Committee. Three levels of data collection are planned to reflect<br />
national, provincial and facility-level diversity. Data presented in this paper reflect work done at<br />
national level.<br />
Individual interviews were conducted with 15 participants at national level. Participants were<br />
purposefully selected from among key staff involved in GHIs at national level as well as amongst<br />
in‐country staff of donors and recipient nongovernmental organizations (NGOs). Senior<br />
government officials and policy makers at the National Department of <strong>Health</strong> (NDOH)<br />
headquarters were interviewed. An attempt was made to maintain a balance across the different<br />
categories.<br />
170