- Page 2 and 3: Table of Contents Key Acronyms Intr
- Page 4 and 5: Policy analysis of the impact of Gl
- Page 6 and 7: OIs Opportunistic infections OVC Or
- Page 8 and 9: core section of the document then p
- Page 10 and 11: Figure 1: Analytic framework for MP
- Page 12 and 13: studies. MPS researchers have linke
- Page 14 and 15: Burundi: Building a health system t
- Page 16 and 17: at between US$ 14.5 and US$ 18.5 pe
- Page 18 and 19: collaborations with European school
- Page 20 and 21: epresent only US$ 1.75 per month pe
- Page 22 and 23: Service Delivery The decentralizati
- Page 24 and 25: Long term HSS will require governme
- Page 26 and 27: Cameroon: Evaluation of the Nationa
- Page 28 and 29: Table 1 Basic Socioeconomic, Demogr
- Page 32 and 33: side effects) were associated with
- Page 34 and 35: Prevention behaviours Nearly half (
- Page 36 and 37: References [1] The World Bank Group
- Page 38 and 39: Out-of-pocket payments account for
- Page 40 and 41: as well as the number of community
- Page 42 and 43: Table 1: Characteristics of facilit
- Page 44 and 45: Table 4: Estimated changes in human
- Page 46 and 47: Central African Republic: Impact of
- Page 48 and 49: Objectives and Methodology In this
- Page 50 and 51: Financing There was a general appre
- Page 52 and 53: NGOs and Civil Society The overall
- Page 54 and 55: Discussion Interviews with key info
- Page 56 and 57: China: The Impact of the Global Fun
- Page 58 and 59: Table 2 Global Health Initiative In
- Page 60 and 61: In Yunnan and Henan, the epidemic i
- Page 62 and 63: funded only from the MOH Pilot Prog
- Page 64 and 65: References [1] China at a glance. W
- Page 66 and 67: 1994, private spending and emergenc
- Page 68 and 69: understanding of their roles and re
- Page 70 and 71: References [1] Human Development Re
- Page 72 and 73: In 2003, the government launched th
- Page 74 and 75: Objectives and Methodology The data
- Page 76 and 77: Health Workforce Ghana is challenge
- Page 78 and 79: Discussion GHIs are critical for ra
- Page 80 and 81:
Haiti: Maximizing Positive Synergie
- Page 82 and 83:
Table 1 Basic Socioeconomic, Demogr
- Page 84 and 85:
with need. With GHI funding, distri
- Page 86 and 87:
I know that within [the organizatio
- Page 88 and 89:
Much of the initial enthusiasm abou
- Page 90 and 91:
services, or for measures of qualit
- Page 92 and 93:
funds and more funding focused on i
- Page 94 and 95:
INDIA: Exploring how disease-specif
- Page 96 and 97:
PEPFAR* Year Amount Disbursed (in U
- Page 98 and 99:
Primary data collection - facility
- Page 100 and 101:
The Global Fund has strengthened th
- Page 102 and 103:
References [1] The World Bank Group
- Page 104 and 105:
Background The Republic of Kenya li
- Page 106 and 107:
Results Leadership and Governance D
- Page 108 and 109:
Informants noted that a general lac
- Page 110 and 111:
time periods. Informants believed t
- Page 112 and 113:
References [1] The World Bank Group
- Page 114 and 115:
A comprehensive, long-term reform o
- Page 116 and 117:
The effects of GHIs on the capacity
- Page 118 and 119:
their budget was comprised of Globa
- Page 120 and 121:
Quality of services The majority of
- Page 122 and 123:
References [1] Kyrgyzstan at a glan
- Page 124 and 125:
Commission (NAC) in 2001 as a multi
- Page 126 and 127:
Objectives and methodology The main
- Page 128 and 129:
Discussion The findings of the Mala
- Page 130 and 131:
Pakistan: The impact of the Global
- Page 132 and 133:
international standards. The Under
- Page 134 and 135:
the US Centers for Disease Control
- Page 136 and 137:
Some negative effects are also attr
- Page 138 and 139:
to country health systems by way of
- Page 140 and 141:
Peru: Effects of the Implementation
- Page 142 and 143:
Table 2 Global Health Initiative In
- Page 144 and 145:
HIV/AIDS, mainly around the Compreh
- Page 146 and 147:
without substantial emphasis on pre
- Page 148 and 149:
References [1] The World Bank Group
- Page 150 and 151:
Rwanda: The Impact of Global Health
- Page 152 and 153:
Rwanda was US$ 584.9 million in 200
- Page 154 and 155:
International Health Partnership, t
- Page 156 and 157:
PEPFAR’s funding practices were l
- Page 158 and 159:
medical staff to higher-paying admi
- Page 160 and 161:
system (CPDS), in which many stakeh
- Page 162 and 163:
needing medical transport. Both GHI
- Page 164 and 165:
Some informants felt that local NGO
- Page 166 and 167:
Senegal: The effects of Global Heal
- Page 168 and 169:
Table 1: Basic Health System and Ep
- Page 170 and 171:
case study. Data analysis was condu
- Page 172 and 173:
of respondents aware of treated net
- Page 174 and 175:
South Africa: The effects of Global
- Page 176 and 177:
Table 2 Global Health Initiative In
- Page 178 and 179:
of South Africa (GHI2, ND6). 26 Don
- Page 180 and 181:
NDOH to disburse external funds in
- Page 182 and 183:
The lack of effective monitoring an
- Page 184 and 185:
Despite these problems, GHI funding
- Page 186 and 187:
[19] The Global Fund for Aids Tuber
- Page 188 and 189:
Official Development Assistance (OD
- Page 190 and 191:
The study employed both purposive s
- Page 192 and 193:
Figure 1: Number of Clinicians at S
- Page 194 and 195:
There were very significant increas
- Page 196 and 197:
GHIs created an opportunity to cond
- Page 198 and 199:
Ukraine: Effects of the Global Fund
- Page 200 and 201:
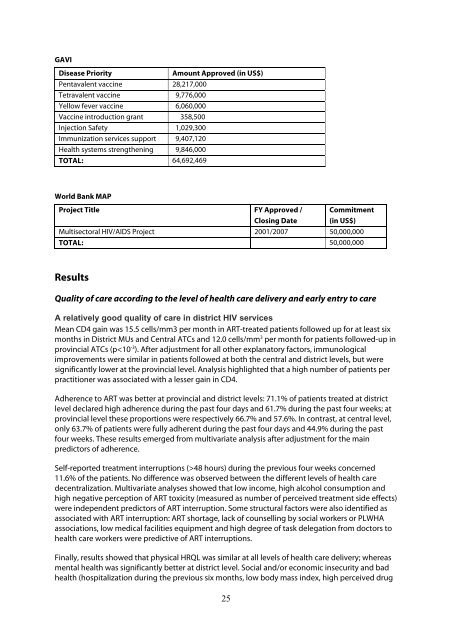
GAVI (in US$) Disease Priority Amou
- Page 202 and 203:
government and nongovernmental prov
- Page 204 and 205:
• The introduction of new service
- Page 206 and 207:
References [1] Data are from the Mi
- Page 208 and 209:
The health system struggles with a
- Page 210 and 211:
Objectives and Methodology This stu
- Page 212 and 213:
Nonetheless, efforts to recruit and
- Page 214 and 215:
References [1] The World Bank Group
- Page 216 and 217:
average annual population growth of
- Page 218 and 219:
2006 149,022,153 2007 216,012,780 2
- Page 220 and 221:
isks duplication of services but al
- Page 222 and 223:
centres have only one qualified hea
- Page 224 and 225:
Policy analysis of the impact of Gl
- Page 226 and 227:
countries” [6]. The TRP apply sev
- Page 228 and 229:
PEPFAR I & II The newest PEPFAR leg
- Page 230 and 231:
Types of fundable HRH interventions
- Page 232 and 233:
Global Fund In two country applicat
- Page 234 and 235:
TABLE 3: Selected Countries: MPS Ca
- Page 236 and 237:
HRH Intervention Categories GAVI: C
- Page 238 and 239:
HRH Intervention Categories GLOBAL
- Page 240 and 241:
HRH Intervention Categories PEPFAR
- Page 242 and 243:
Conclusion: Directions for future r
- Page 244 and 245:
GHIs and health systems. Civil soci
- Page 246 and 247:
Annex 01: Data sources for tables i
- Page 248 and 249:
Annex 02: Contributing Institutions