The Global Water Crisis: Addressing an Urgent Security - Unu-inweh ...
The Global Water Crisis: Addressing an Urgent Security - Unu-inweh ...
The Global Water Crisis: Addressing an Urgent Security - Unu-inweh ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
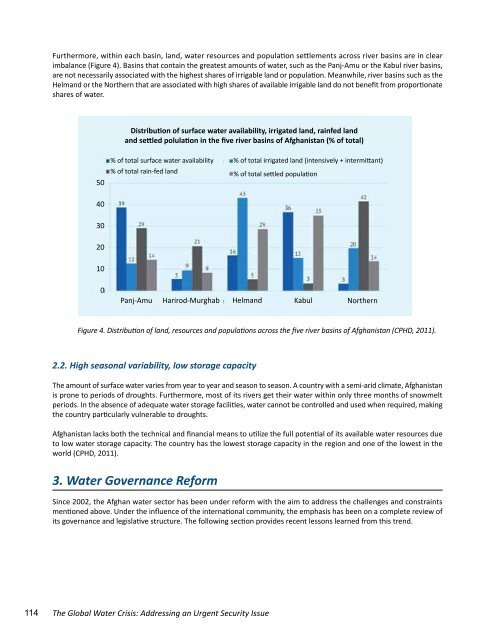
Furthermore, within each basin, l<strong>an</strong>d, water resources <strong>an</strong>d population settlements across river basins are in clear<br />
imbal<strong>an</strong>ce (Figure 4). Basins that contain the greatest amounts of water, such as the P<strong>an</strong>j-Amu or the Kabul river basins,<br />
are not necessarily associated with the highest shares of irrigable l<strong>an</strong>d or population. Me<strong>an</strong>while, river basins such as the<br />
Helm<strong>an</strong>d or the Northern that are associated with high shares of available irrigable l<strong>an</strong>d do not benefit from proportionate<br />
shares of water.<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
Distribution of surface water availability, irrigated l<strong>an</strong>d, rainfed l<strong>an</strong>d<br />
<strong>an</strong>d settled polulation in the five river basins of Afgh<strong>an</strong>ist<strong>an</strong> (% of total)<br />
% of total surface water availability<br />
% of total rain-fed l<strong>an</strong>d<br />
Figure 4. Distribution of l<strong>an</strong>d, resources <strong>an</strong>d populations across the five river basins of Afgh<strong>an</strong>ist<strong>an</strong> (CPHD, 2011).<br />
2.2. High seasonal variability, low storage capacity<br />
<strong>The</strong> amount of surface water varies from year to year <strong>an</strong>d season to season. A country with a semi-arid climate, Afgh<strong>an</strong>ist<strong>an</strong><br />
is prone to periods of droughts. Furthermore, most of its rivers get their water within only three months of snowmelt<br />
periods. In the absence of adequate water storage facilities, water c<strong>an</strong>not be controlled <strong>an</strong>d used when required, making<br />
the country particularly vulnerable to droughts.<br />
Afgh<strong>an</strong>ist<strong>an</strong> lacks both the technical <strong>an</strong>d fin<strong>an</strong>cial me<strong>an</strong>s to utilize the full potential of its available water resources due<br />
to low water storage capacity. <strong>The</strong> country has the lowest storage capacity in the region <strong>an</strong>d one of the lowest in the<br />
world (CPHD, 2011).<br />
3. <strong>Water</strong> Govern<strong>an</strong>ce Reform<br />
Since 2002, the Afgh<strong>an</strong> water sector has been under reform with the aim to address the challenges <strong>an</strong>d constraints<br />
mentioned above. Under the influence of the international community, the emphasis has been on a complete review of<br />
its govern<strong>an</strong>ce <strong>an</strong>d legislative structure. <strong>The</strong> following section provides recent lessons learned from this trend.<br />
114 <strong>The</strong> <strong>Global</strong> <strong>Water</strong> <strong>Crisis</strong>: <strong>Addressing</strong> <strong>an</strong> <strong>Urgent</strong> <strong>Security</strong> Issue<br />
% of total irrigated l<strong>an</strong>d (intensively + intermitt<strong>an</strong>t)<br />
% of total settled population<br />
P<strong>an</strong>j-Amu Harirod-Murghab Helm<strong>an</strong>d Kabul Northern