Resistencia de materiales - Ver más Ya.com
Resistencia de materiales - Ver más Ya.com
Resistencia de materiales - Ver más Ya.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
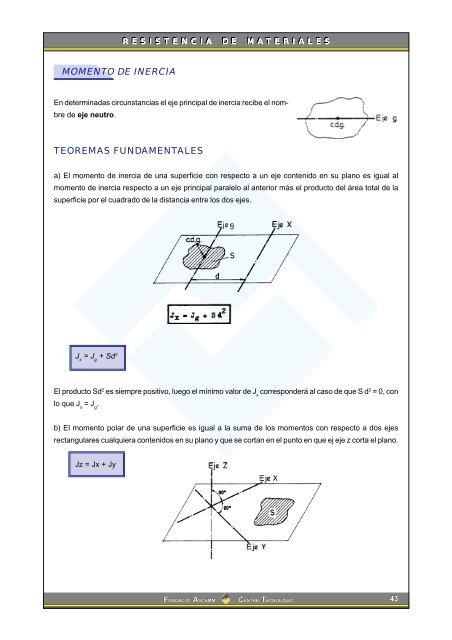
MOMENTO DE INERCIA<br />
RESISTENCIA RESISTENCIA RESISTENCIA DE DE DE MA MATERIALES<br />
MA MATERIALES<br />
MA TERIALES<br />
TERIALES<br />
TERIALES<br />
En <strong>de</strong>terminadas circunstancias el eje principal <strong>de</strong> inercia recibe el nombre<br />
<strong>de</strong> eje neutro.<br />
TEOREMAS FUNDAMENTALES<br />
a) El momento <strong>de</strong> inercia <strong>de</strong> una superficie con respecto a un eje contenido en su plano es igual al<br />
momento <strong>de</strong> inercia respecto a un eje principal paralelo al anterior <strong>más</strong> el producto <strong>de</strong>l área total <strong>de</strong> la<br />
superficie por el cuadrado <strong>de</strong> la distancia entre los dos ejes.<br />
J x = J g + Sd 2<br />
El producto Sd2 es siempre positivo, luego el mínimo valor <strong>de</strong> J correspon<strong>de</strong>rá al caso <strong>de</strong> que S d x 2 = 0, con<br />
lo que J = J . x g<br />
b) El momento polar <strong>de</strong> una superficie es igual a la suma <strong>de</strong> los momentos con respecto a dos ejes<br />
rectangulares cualquiera contenidos en su plano y que se cortan en el punto en que ej eje z corta el plano.<br />
Jz = Jx + Jy<br />
FUNDACIÓ ASCAMM CENTRE TECNOLÒGIC<br />
43