You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
COSMOS: Complete Online <strong>Sol</strong>utions Manual Organization System<br />
Chapter 2, <strong>Sol</strong>ution 110.<br />
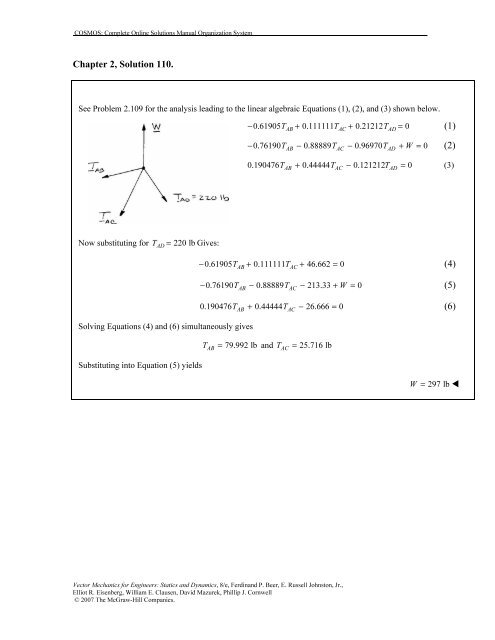
See Problem 2.109 for the analysis leading to the linear algebraic Equations (1), (2), and (3) shown below.<br />
− 0.61905T + 0.111111T + 0.21212T<br />
= 0 (1)<br />
AB AC AD<br />
−0.76190T − 0.88889T − 0.96970T + W = 0 (2)<br />
AB AC AD<br />
0.190476T + 0.44444T − 0.121212T<br />
= 0 (3)<br />
AB AC AD<br />
Now substituting for T = 220 lb Gives:<br />
AD<br />
<strong>Sol</strong>ving Equations (4) and (6) simultaneously gives<br />
− 0.61905T<br />
+ 0.111111T<br />
+ 46.662 = 0<br />
(4)<br />
AB<br />
AC<br />
−0.76190T − 0.88889T − 213.33 + W = 0<br />
(5)<br />
AB<br />
AC<br />
0.190476T<br />
+ 0.44444T<br />
− 26.666 = 0<br />
(6)<br />
AB<br />
AC<br />
T = 79.992 lb and T = 25.716 lb<br />
AB<br />
Substituting into Equation (5) yields<br />
W = 297 lb ⊳<br />
AC<br />
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics, 8/e, Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston, Jr.,<br />
Elliot R. Eisenberg, William E. Clausen, David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell<br />
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies.