UN World Investment Report 2010 - Office of Trade Negotiations
UN World Investment Report 2010 - Office of Trade Negotiations
UN World Investment Report 2010 - Office of Trade Negotiations
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
42<br />
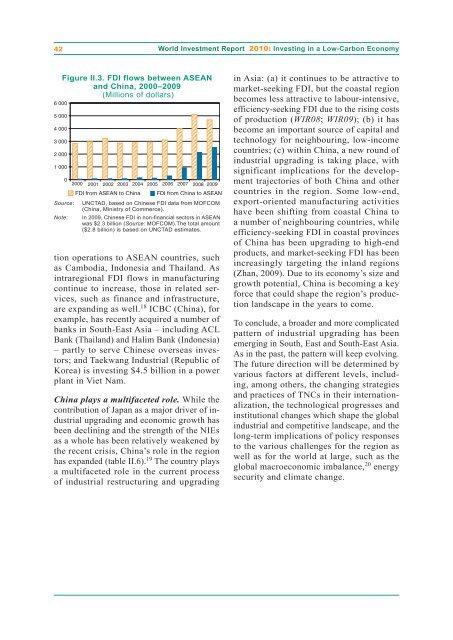
Figure II.3. FDI flows between ASEAN<br />
and China, 2000–2009<br />
(Millions <strong>of</strong> dollars)<br />
6 000<br />
5 000<br />
4 000<br />
3 000<br />
2 000<br />
1 000<br />
0<br />
2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009<br />
FDI from ASEAN to China FDI from China to ASEAN<br />
Source: <strong>UN</strong>CTAD, based on Chinese FDI data from MOFCOM<br />
(China, Ministry <strong>of</strong> Commerce).<br />
Note: In 2009, Chinese FDI in non-financial sectors in ASEAN<br />
was $2.3 billion (Source: MOFCOM).The total amount<br />
($2.8 billion) is based on <strong>UN</strong>CTAD estimates.<br />
tion operations to ASEAN countries, such<br />
as Cambodia, Indonesia and Thailand. As<br />
intraregional FDI flows in manufacturing<br />
continue to increase, those in related services,<br />
such as finance and infrastructure,<br />
are expanding as well. 18 ICBC (China), for<br />
example, has recently acquired a number <strong>of</strong><br />
banks in South-East Asia – including ACL<br />
Bank (Thailand) and Halim Bank (Indonesia)<br />
– partly to serve Chinese overseas investors;<br />
and Taekwang Industrial (Republic <strong>of</strong><br />
Korea) is investing $4.5 billion in a power<br />
plant in Viet Nam.<br />
China plays a multifaceted role. While the<br />
contribution <strong>of</strong> Japan as a major driver <strong>of</strong> industrial<br />
upgrading and economic growth has<br />
been declining and the strength <strong>of</strong> the NIEs<br />
as a whole has been relatively weakened by<br />
the recent crisis, China’s role in the region<br />
has expanded (table II.6). 19 The country plays<br />
a multifaceted role in the current process<br />
<strong>of</strong> industrial restructuring and upgrading<br />
<strong>World</strong> <strong>Investment</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>2010</strong>: Investing in a Low-Carbon Economy<br />
in Asia: (a) it continues to be attractive to<br />
market-seeking FDI, but the coastal region<br />
becomes less attractive to labour-intensive,<br />
efficiency-seeking FDI due to the rising costs<br />
<strong>of</strong> production (WIR08; WIR09); (b) it has<br />
become an important source <strong>of</strong> capital and<br />
technology for neighbouring, low-income<br />
countries; (c) within China, a new round <strong>of</strong><br />
industrial upgrading is taking place, with<br />
significant implications for the development<br />
trajectories <strong>of</strong> both China and other<br />
countries in the region. Some low-end,<br />
export-oriented manufacturing activities<br />
have been shifting from coastal China to<br />
a number <strong>of</strong> neighbouring countries, while<br />
efficiency-seeking FDI in coastal provinces<br />
<strong>of</strong> China has been upgrading to high-end<br />
products, and market-seeking FDI has been<br />
increasingly targeting the inland regions<br />
(Zhan, 2009). Due to its economy’s size and<br />
growth potential, China is becoming a key<br />
force that could shape the region’s production<br />
landscape in the years to come.<br />
To conclude, a broader and more complicated<br />
pattern <strong>of</strong> industrial upgrading has been<br />
emerging in South, East and South-East Asia.<br />
As in the past, the pattern will keep evolving.<br />
The future direction will be determined by<br />
various factors at different levels, including,<br />
among others, the changing strategies<br />
and practices <strong>of</strong> TNCs in their internationalization,<br />
the technological progresses and<br />
institutional changes which shape the global<br />
industrial and competitive landscape, and the<br />
long-term implications <strong>of</strong> policy responses<br />
to the various challenges for the region as<br />
well as for the world at large, such as the<br />
global macroeconomic imbalance, 20 energy<br />
security and climate change.