Martis Valley Groundwater Management Plan - Placer County Water ...
Martis Valley Groundwater Management Plan - Placer County Water ...
Martis Valley Groundwater Management Plan - Placer County Water ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
utilized a water balance method to estimate ground water recharge to the <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> Ground <strong>Water</strong><br />
Basin of approximately 18,000 ac-ft/yr. In 2001 Nimbus Engineers used a water balance approach to<br />
compute a recharge value of 24,700 ac-ft/yr to the ground water basin. Kennedy/Jenks Consultants in<br />
2001 published a report titled “Independent Appraisal of <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> Ground <strong>Water</strong> Availability,<br />
Nevada and <strong>Placer</strong> Counties, California” where they concluded that the earlier studies by Hydro-Search,<br />
Inc (1974 and updates) and Nimbus Engineers (2001) were conservative, as the total amount of ground<br />
water discharge to streams was considered under predicted; however, updated recharge estimates were not<br />
provided in this report. Interflow Hydrology, Inc. and Cordilleran Hydrology, Inc. prepared a 2003 report<br />
indicating that ground water discharge to tributary Truckee River streams in the <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> Ground<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Basin is 34,560 ac-ft/yr, of which approximately 24,240 ac-ft/yr is contributed by high altitude<br />
areas of the basin (e.g., in the vicinity of Northstar) and the remaining 10,320 ac-ft/yr occurs in lower<br />
elevation areas. In summary, previous recharge estimates based on water balance approaches range from<br />
18,000 to 34,560 ac-ft/yr.<br />
Description of PRMS Recharge Method<br />
The PRMS model (Leavesley et al., 1983) is driven by daily values of precipitation and<br />
maximum and minimum air temperature, and simulates snow accumulation, ablation, canopy<br />
interception, evapotranspiration, surface runoff, infiltration, water storage in the soil zone and deep<br />
percolation through the bottom of the root or soil zone – PRMS recharge is defined as the model<br />
computed excess water leaving the root or soil zone after abstractions for surface runoff and<br />
evapotranspiration are accounted for (Figure 1). The system is modeled in its natural transient state from<br />
1981 to 2011. Reservoir operations, irrigation within the basin, septic drainfields, and diversion of effluent<br />
to the Truckee Tahoe Sanitation Agency and subsequent release of treated effluent to the Truckee River<br />
are not explicitly simulated in the model. However, the <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> PRMS model utilizes naturalized<br />
flows that remove the effects of reservoir operations during model calibration.<br />
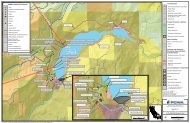
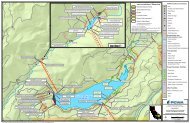
The current PRMS model developed for <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> encompasses the entire <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong><br />
hydrologic basin (Figure 2), and is subdivided into 14 watersheds for model calibration to internal stream<br />
gauges. Computation of recharge for the <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> Ground <strong>Water</strong> Basin requires aggregation of the<br />
PRMS results for all cells within the delineated ground water basin (Figure 3). The model domain was<br />
discretized into square grid cells of 300 m resolution; each of these cells represents a hydrologic response<br />
unit (HRU). The model is parameterized from the National Elevation Dataset (NED), STATSGO soils<br />
database, and USGS land use land cover (LULC) dataset. The depth of the root or soil zone is determined<br />
by the LULC of the HRU. Five categories of LULC are used to assign these depths viz. bare soils,<br />
grasses, shrubs, trees, and water. For the category water, recharge is assumed zero.<br />
Daily weather data from the Truckee #2 SNOTEL site is used to drive the PRMS model. This<br />
station is used to develop monthly ratios based on PRISM maps to distribute precipitation over the entire<br />
basin. To account for days when temperature inversions within the valley occur, an additional weather<br />
station, Mt. Rose SNOTEL, is implemented.<br />
PRMS Recharge Estimates<br />
The estimated mean annual ground water recharge for the <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> Ground <strong>Water</strong> Basin<br />
computed from PRMS is presented in Figure 4. PRMS simulated recharge varies from year to year based<br />
Page 2 of 11