Martis Valley Groundwater Management Plan - Placer County Water ...
Martis Valley Groundwater Management Plan - Placer County Water ...
Martis Valley Groundwater Management Plan - Placer County Water ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Section 2<br />
Physical Setting<br />
The MVGB is located in the transition zone between the Sierra Nevada and the Basin and Range<br />
Geomorphic Provinces, east of the Sierra Nevada crest and part of the larger Tahoe-Truckee River Basin<br />
of California and Nevada. <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> is the principal topographic feature within the MVGB. The<br />
surrounding landscape is mountainous, underlain by volcanic and, to some extent, granitic bedrock, with<br />
apparent faulting and some portions that have been glaciated. A significant portion of the land within the<br />
MVGB boundary is privately owned with some areas managed as forest, open space and/or for<br />
recreation by special districts or agencies, including the U.S. Forest Service. This section of the GMP<br />
characterizes the physical setting of the MVGB, including: topography, climate, surface water hydrology,<br />
geology, hydrogeology, and water use.<br />
2.1 Topography<br />
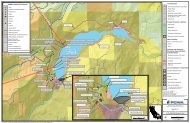
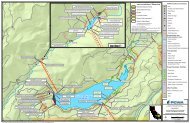
The MVGB encompasses roughly 57 square miles, and lies within the Middle Truckee River <strong>Water</strong>shed.<br />
Elevations of the valley floor range from 5,700 to 5,900 feet above mean sea level (msl). The valley is<br />
accented by hills rising above the valley floor and mountains to the south and east of the valley. High<br />
points within or immediately adjacent to the MVGB include Bald Mountain at an elevation of 6,760 feet<br />
and Alder Hill at 6,733 feet, located on the western margin of the MVGB, and Lookout Mountain at<br />
8,104 feet and Mt. Pluto at 8,617 feet, located on its the southern fringe. <strong>Martis</strong> Peak, further to the<br />
east, is at 8,742 feet. Figure 2-1 illustrates the MVGB location and topography.<br />
2.2 Climate<br />
The Tahoe-Truckee region experiences warm and dry summers, and cold, wet and snowy winters.<br />
Elevation and rain shadow play major roles in the spatial distribution of temperature and precipitation.<br />
Precipitation is highest at upper elevations in the western portion of the basin, toward the Sierra Crest,<br />
and decreases with elevation in the eastern portion of the basin (Figure 2-2). Mean annual precipitation<br />
(as snow water equivalent) ranges from approximately 30 inches below 6,500 feet to over 45 inches<br />
above 6,500 feet. Precipitation falls mostly as snow between October and April, though runoff and<br />
streamflow also responds to periodic mid-winter rain-on-snow events. Annual peak streamflow typically<br />
occurs during spring snowmelt in May or June. A small proportion of the total annual precipitation falls<br />
during brief thunderstorms in the summer months. Average monthly precipitation is shown in Figure 2-3,<br />
as recorded at the United States Forest Service (USFS) Truckee Ranger Station, near the center of the<br />
watershed (California Data Exchange Center Station TKE). Average temperatures range from daily lows<br />
of 15ºF in December and January to daily highs of 82ºF in July, as recorded at SNOTEL Station<br />
Truckee #2.<br />
DRAFT for review purposes only. Use of contents on this sheet is subject to the limitations specified at the end of this document.<br />
P:\40000\140691 - PCWA <strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> GWP\GMP\Report\3rd Draft\<strong>Martis</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> GMP Draft 01-09-13.docx<br />
2-1