Rating Models and Validation - Oesterreichische Nationalbank
Rating Models and Validation - Oesterreichische Nationalbank
Rating Models and Validation - Oesterreichische Nationalbank
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Rating</strong> <strong>Models</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Validation</strong><br />
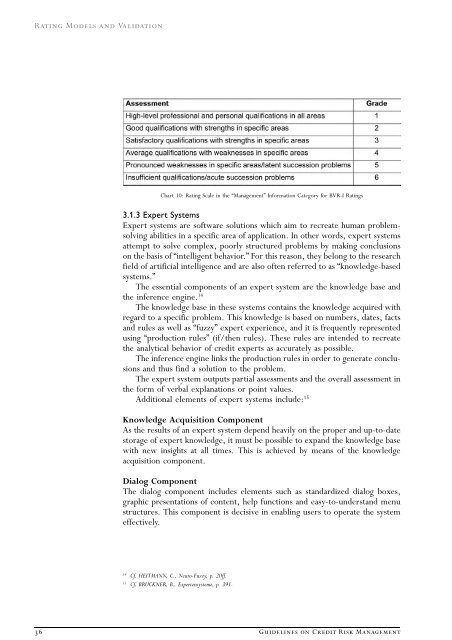
Chart 10: <strong>Rating</strong> Scale in the ÒManagementÓ Information Category for BVR-I <strong>Rating</strong>s<br />
3.1.3 Expert Systems<br />
Expert systems are software solutions which aim to recreate human problemsolving<br />
abilities in a specific area of application. In other words, expert systems<br />
attempt to solve complex, poorly structured problems by making conclusions<br />
on the basis of Òintelligent behavior.Ó For this reason, they belong to the research<br />
field of artificial intelligence <strong>and</strong> are also often referred to as Òknowledge-based<br />
systems.Ó<br />
The essential components of an expert system are the knowledge base <strong>and</strong><br />
the inference engine. 14<br />
The knowledge base in these systems contains the knowledge acquired with<br />
regard to a specific problem. This knowledge is based on numbers, dates, facts<br />
<strong>and</strong> rules as well as ÒfuzzyÓ expert experience, <strong>and</strong> it is frequently represented<br />
using Òproduction rulesÓ (if/then rules). These rules are intended to recreate<br />
the analytical behavior of credit experts as accurately as possible.<br />
The inference engine links the production rules in order to generate conclusions<br />
<strong>and</strong> thus find a solution to the problem.<br />
The expert system outputs partial assessments <strong>and</strong> the overall assessment in<br />
the form of verbal explanations or point values.<br />
Additional elements of expert systems include: 15<br />
Knowledge Acquisition Component<br />
As the results of an expert system depend heavily on the proper <strong>and</strong> up-to-date<br />
storage of expert knowledge, it must be possible to exp<strong>and</strong> the knowledge base<br />
with new insights at all times. This is achieved by means of the knowledge<br />
acquisition component.<br />
Dialog Component<br />
The dialog component includes elements such as st<strong>and</strong>ardized dialog boxes,<br />
graphic presentations of content, help functions <strong>and</strong> easy-to-underst<strong>and</strong> menu<br />
structures. This component is decisive in enabling users to operate the system<br />
effectively.<br />
14 Cf. HEITMANN, C., Neuro-Fuzzy, p. 20ff.<br />
15 Cf. BRUCKNER, B., Expertensysteme, p. 391.<br />
36 Guidelines on Credit Risk Management