Carbon dioxide removal in indirect gasification - SGC
Carbon dioxide removal in indirect gasification - SGC
Carbon dioxide removal in indirect gasification - SGC
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>SGC</strong> Rapport 2013:277<br />
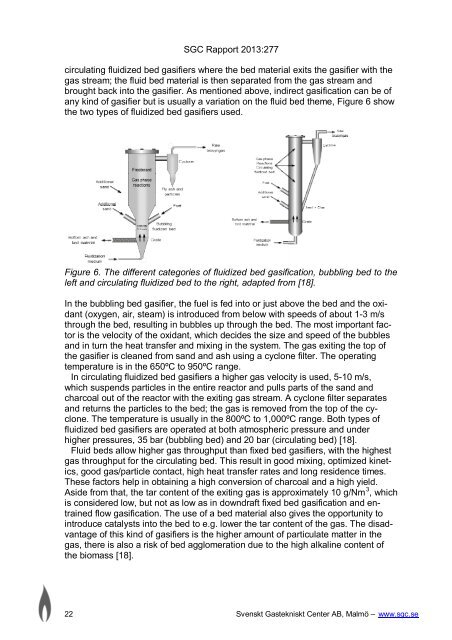
circulat<strong>in</strong>g fluidized bed gasifiers where the bed material exits the gasifier with the<br />
gas stream; the fluid bed material is then separated from the gas stream and<br />
brought back <strong>in</strong>to the gasifier. As mentioned above, <strong>in</strong>direct <strong>gasification</strong> can be of<br />
any k<strong>in</strong>d of gasifier but is usually a variation on the fluid bed theme, Figure 6 show<br />
the two types of fluidized bed gasifiers used.<br />
Figure 6. The different categories of fluidized bed <strong>gasification</strong>, bubbl<strong>in</strong>g bed to the<br />
left and circulat<strong>in</strong>g fluidized bed to the right, adapted from [18].<br />
In the bubbl<strong>in</strong>g bed gasifier, the fuel is fed <strong>in</strong>to or just above the bed and the oxidant<br />
(oxygen, air, steam) is <strong>in</strong>troduced from below with speeds of about 1-3 m/s<br />
through the bed, result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> bubbles up through the bed. The most important factor<br />
is the velocity of the oxidant, which decides the size and speed of the bubbles<br />
and <strong>in</strong> turn the heat transfer and mix<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the system. The gas exit<strong>in</strong>g the top of<br />
the gasifier is cleaned from sand and ash us<strong>in</strong>g a cyclone filter. The operat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
temperature is <strong>in</strong> the 650ºC to 950ºC range.<br />
In circulat<strong>in</strong>g fluidized bed gasifiers a higher gas velocity is used, 5-10 m/s,<br />
which suspends particles <strong>in</strong> the entire reactor and pulls parts of the sand and<br />
charcoal out of the reactor with the exit<strong>in</strong>g gas stream. A cyclone filter separates<br />
and returns the particles to the bed; the gas is removed from the top of the cyclone.<br />
The temperature is usually <strong>in</strong> the 800ºC to 1,000ºC range. Both types of<br />
fluidized bed gasifiers are operated at both atmospheric pressure and under<br />
higher pressures, 35 bar (bubbl<strong>in</strong>g bed) and 20 bar (circulat<strong>in</strong>g bed) [18].<br />
Fluid beds allow higher gas throughput than fixed bed gasifiers, with the highest<br />
gas throughput for the circulat<strong>in</strong>g bed. This result <strong>in</strong> good mix<strong>in</strong>g, optimized k<strong>in</strong>etics,<br />
good gas/particle contact, high heat transfer rates and long residence times.<br />
These factors help <strong>in</strong> obta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g a high conversion of charcoal and a high yield.<br />
Aside from that, the tar content of the exit<strong>in</strong>g gas is approximately 10 g/Nm 3 , which<br />
is considered low, but not as low as <strong>in</strong> downdraft fixed bed <strong>gasification</strong> and entra<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
flow <strong>gasification</strong>. The use of a bed material also gives the opportunity to<br />
<strong>in</strong>troduce catalysts <strong>in</strong>to the bed to e.g. lower the tar content of the gas. The disadvantage<br />
of this k<strong>in</strong>d of gasifiers is the higher amount of particulate matter <strong>in</strong> the<br />
gas, there is also a risk of bed agglomeration due to the high alkal<strong>in</strong>e content of<br />
the biomass [18].<br />
22 Svenskt Gastekniskt Center AB, Malmö – www.sgc.se