Carbon dioxide removal in indirect gasification - SGC
Carbon dioxide removal in indirect gasification - SGC
Carbon dioxide removal in indirect gasification - SGC
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>SGC</strong> Rapport 2013:277<br />
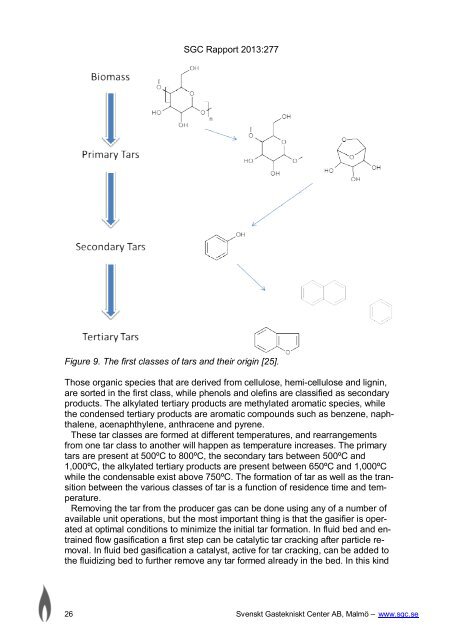
Figure 9. The first classes of tars and their orig<strong>in</strong> [25].<br />
Those organic species that are derived from cellulose, hemi-cellulose and lign<strong>in</strong>,<br />
are sorted <strong>in</strong> the first class, while phenols and olef<strong>in</strong>s are classified as secondary<br />
products. The alkylated tertiary products are methylated aromatic species, while<br />
the condensed tertiary products are aromatic compounds such as benzene, naphthalene,<br />
acenaphthylene, anthracene and pyrene.<br />
These tar classes are formed at different temperatures, and rearrangements<br />
from one tar class to another will happen as temperature <strong>in</strong>creases. The primary<br />
tars are present at 500ºC to 800ºC, the secondary tars between 500ºC and<br />
1,000ºC, the alkylated tertiary products are present between 650ºC and 1,000ºC<br />
while the condensable exist above 750ºC. The formation of tar as well as the transition<br />
between the various classes of tar is a function of residence time and temperature.<br />
Remov<strong>in</strong>g the tar from the producer gas can be done us<strong>in</strong>g any of a number of<br />
available unit operations, but the most important th<strong>in</strong>g is that the gasifier is operated<br />
at optimal conditions to m<strong>in</strong>imize the <strong>in</strong>itial tar formation. In fluid bed and entra<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
flow <strong>gasification</strong> a first step can be catalytic tar crack<strong>in</strong>g after particle <strong>removal</strong>.<br />
In fluid bed <strong>gasification</strong> a catalyst, active for tar crack<strong>in</strong>g, can be added to<br />
the fluidiz<strong>in</strong>g bed to further remove any tar formed already <strong>in</strong> the bed. In this k<strong>in</strong>d<br />
26 Svenskt Gastekniskt Center AB, Malmö – www.sgc.se