Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
STRABISMUS<br />
overacting in a V pattern. If there is no<br />
oblique overaction, transpose the horizontal<br />
recti, the medial recti to the apex <strong>of</strong> the<br />
pattern, and the lateral recti to the base.<br />
4. Oblique surgery in the adult is less forgiving<br />
than in the child.<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
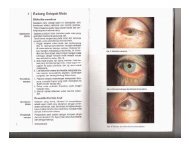
Figure 7.11 Underaction <strong>of</strong> left superior oblique in<br />
child with left coronal synostosis. Tightening superior<br />
oblique tendon laxity improved field <strong>of</strong> binocular<br />
single vision with improved ocular posture without<br />
an acquired Brown’s syndrome. (a) Preoperative.<br />
(b) postoperative<br />
Adjustable sutures<br />
Adjustable sutures increase the chance <strong>of</strong><br />
ideal surgical alignment with one operation,<br />
decreasing the need for reoperation or staged<br />
repairs. More sophisticated surgical techniques<br />
and materials have stimulated their increased<br />
use. Different techniques involve two-stage<br />
procedures where the final alignment is achieved<br />
postoperatively with external sutures, or the<br />
procedure completed with the patient awake. 17<br />
In our experience, using adjustable sutures has<br />
led to better judgement in the operating room,<br />
leading to a minority <strong>of</strong> patients needing further<br />
postoperative adjustment (Figure 7.12).<br />
preferred to superior oblique tucks. In neurogenic<br />
cases ipsilateral superior rectus recession is useful<br />
where a long-standing superior oblique palsy has<br />
resulted in tightness <strong>of</strong> the tendon <strong>of</strong> the superior<br />
rectus. The superior oblique tightening procedure<br />
(Harada–Ito) is our preferred option where<br />
torsion is the main problem.<br />
Summary <strong>of</strong> management<br />
<strong>of</strong> A and V patterns<br />
1. Observe the vertical movements <strong>of</strong> the eyes<br />
with accommodation controlled, preferably<br />
doing the test at distance and asking the<br />
patient to maintain fixation by depressing<br />
and elevating the chin. The eyes will move in<br />
the opposite directions and measurements<br />
can be made.<br />
2. Consider whether the pattern is severe<br />
enough to treat.<br />
3. Operate on the superior obliques if overacting<br />
in an A pattern and inferior obliques if<br />
Botulinum chemodenervation<br />
Studies have shown botulinum toxin to be<br />
helpful in small to moderate esotropia and<br />
exotropia (less than 40 D), active thyroid disease<br />
if surgery is inappropriate and postoperative<br />
residual strabismus after several weeks. There<br />
has been less evidence for use in A and V<br />
patterns, DVD or oblique muscle disorders.<br />
Success has ranged from 30% to 70% depending<br />
on the size <strong>of</strong> deviation. 18<br />
Sequelae and complications <strong>of</strong><br />
strabismus surgery<br />
Anaesthesia<br />
In early childhood, an anaesthetist well<br />
experienced in paediatric anaesthesia is<br />
essential. Usually day surgery is all that is<br />
required. Children need to be prepared for<br />
hospital, to have their favourite toy with them<br />
and to have their parents with them during<br />
86








![SISTEM SENSORY [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/20667975/1/190x245/sistem-sensory-compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)