Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
STRABISMUS<br />
Normal<br />
R<br />
L<br />
Normal binocular<br />
vision with bifoveal<br />
fixation. Normal retinal<br />
correspondence (NRC)<br />
0° 15° 30° 45°<br />
Mon<strong>of</strong>ixation<br />
syndrome<br />
R<br />
L<br />
<strong>Strabismus</strong> with<br />
abnormal retinal<br />
correspondence (ARC)<br />
and suppression <strong>of</strong> left<br />
macula when viewed<br />
binocularly<br />
45° 30°15° 0°<br />
R<br />
Exotropia with<br />
diplopia<br />
(normal retinal<br />
correspondence)<br />
Esotropia with<br />
diplopia<br />
(normal retinal<br />
correspondence)<br />
Suppression <strong>of</strong><br />
left eye<br />
R<br />
R<br />
L<br />
L<br />
<strong>Strabismus</strong> with<br />
normal macular<br />
function and no<br />
suppression<br />
<strong>Strabismus</strong> and left<br />
amblyopia without<br />
ARC<br />
Figure 6.11<br />
The Hirschberg corneal light reflex test<br />
Krimsky test<br />
The Krimsky test uses a prism bar to equalise<br />
the position <strong>of</strong> the light reflex from each eye; half<br />
the number <strong>of</strong> prism dioptres <strong>of</strong> the deviation<br />
equals magnitude <strong>of</strong> the deviation in degrees<br />
(Figure 6.12).<br />
Figure 6.10 Bagolini striated glasses consist <strong>of</strong> two<br />
plano lenses (one for each eye) with parallel striations<br />
for one eye set at right angles to the striations for the<br />
other. The patient views a light at 6 m through the<br />
glasses. If there is normal binocular vision the light is<br />
perceived as two lines at right angles to each other<br />
passing through the centre <strong>of</strong> each other. As the test is<br />
done in free space, the patient is aware <strong>of</strong> peripheral<br />
objects surrounding the light which optimise the<br />
association between the two eyes, allowing the most<br />
natural environment for testing. In MFS, the fovea <strong>of</strong><br />
the non-dominant eye is suppressed under binocular<br />
conditions. The cross is seen because <strong>of</strong> peripheral<br />
fusion<br />
Motor evaluation – eye movements and<br />
alignment<br />
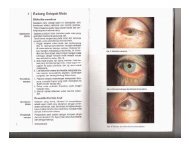
Hirschberg corneal light reflex test<br />
Estimation <strong>of</strong> the corneal light reflex is one <strong>of</strong><br />
the simplest tests <strong>of</strong> ocular alignment. When<br />
testing the corneal light reflex both the source <strong>of</strong><br />
light and the target should be held together. A<br />
small nasal displacement <strong>of</strong> the corneal light<br />
reflex is not uncommon in young children<br />
(Figure 6.11).<br />
Bruckner test<br />
This test determines the presence <strong>of</strong> a<br />
strabismus in the uncooperative child who may<br />
not tolerate cover tests. A test light beam is held<br />
at 1 m and the brightness <strong>of</strong> the red reflex in<br />
each eye is compared. If the red reflex is brighter<br />
in one eye than the other, then it is likely that<br />
strabismus is present in the eye with the brighter<br />
reflex. The disturbance <strong>of</strong> the accommodation<br />
component <strong>of</strong> the near reflex raises a doubt that<br />
the Bruckner test can be relied upon under<br />
2 months <strong>of</strong> age. The reason lies in the smaller<br />
pupil and poorer central vision in newborns who<br />
have a greater depth <strong>of</strong> focus than adults, and as<br />
accommodation does not need to be as exact,<br />
this in turn affects the accuracy <strong>of</strong> the test. We<br />
have found that it is useful after the age <strong>of</strong> 4<br />
months but it has been argued that it is not<br />
completely reliable until after 8 months. 9<br />
15 D base out prism test<br />
The 15 D base out prism test is a useful test<br />
in infants. It stresses the binocular fusion by<br />
64








![SISTEM SENSORY [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/20667975/1/190x245/sistem-sensory-compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)