Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
STRABISMUS<br />
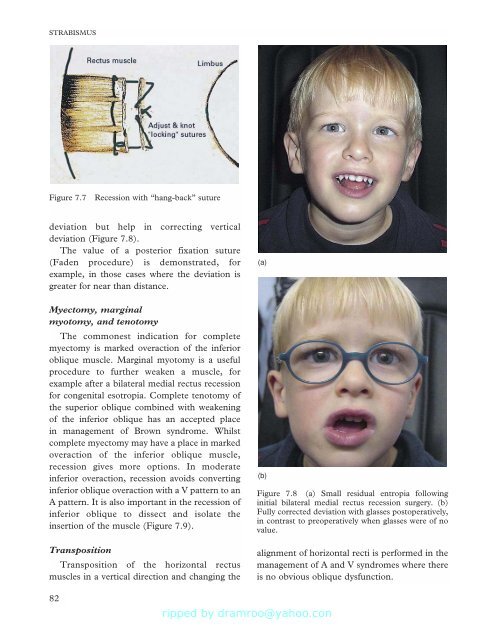
Figure 7.7<br />
Recession with “hang-back” suture<br />
deviation but help in correcting vertical<br />
deviation (Figure 7.8).<br />
The value <strong>of</strong> a posterior fixation suture<br />
(Faden procedure) is demonstrated, for<br />
example, in those cases where the deviation is<br />
greater for near than distance.<br />
Myectomy, marginal<br />
myotomy, and tenotomy<br />
The commonest indication for complete<br />
myectomy is marked overaction <strong>of</strong> the inferior<br />
oblique muscle. Marginal myotomy is a useful<br />
procedure to further weaken a muscle, for<br />
example after a bilateral medial rectus recession<br />
for congenital esotropia. Complete tenotomy <strong>of</strong><br />
the superior oblique combined with weakening<br />
<strong>of</strong> the inferior oblique has an accepted place<br />
in management <strong>of</strong> Brown syndrome. Whilst<br />
complete myectomy may have a place in marked<br />
overaction <strong>of</strong> the inferior oblique muscle,<br />
recession gives more options. In moderate<br />
inferior overaction, recession avoids converting<br />
inferior oblique overaction with a V pattern to an<br />
A pattern. It is also important in the recession <strong>of</strong><br />
inferior oblique to dissect and isolate the<br />
insertion <strong>of</strong> the muscle (Figure 7.9).<br />
Transposition<br />
Transposition <strong>of</strong> the horizontal rectus<br />
muscles in a vertical direction and changing the<br />
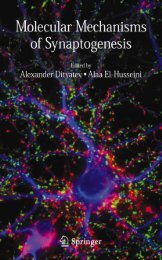
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
Figure 7.8 (a) Small residual entropia following<br />
initial bilateral medial rectus recession surgery. (b)<br />
Fully corrected deviation with glasses postoperatively,<br />
in contrast to preoperatively when glasses were <strong>of</strong> no<br />
value.<br />
alignment <strong>of</strong> horizontal recti is performed in the<br />
management <strong>of</strong> A and V syndromes where there<br />
is no obvious oblique dysfunction.<br />
82







![SISTEM SENSORY [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/20667975/1/190x245/sistem-sensory-compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)