Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
STRABISMUS<br />
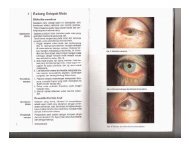
Figure 4.19 Left traumatic fourth nerve palsy<br />
demonstrating weakness <strong>of</strong> left superior oblique<br />
muscle. Note left hypertropia, worse in right gaze and<br />
left head tilt (Bielschowsky head tilt test). Note also<br />
traumatic left mydriasis<br />
(a) (b) (c)<br />
(d) (e) (f)<br />
(g) (h) (i)<br />
Figure 4.20 Child with bilateral Brown’s syndrome. Note in right and left gaze the adducting eye turns down<br />
and is unable to elevate due to tightness <strong>of</strong> the superior oblique tendon. Note also in moving from depression to<br />
elevation in the mid-line the pattern <strong>of</strong> movement is a V due to the eye pivoting about the anchored attachment<br />
<strong>of</strong> the superior oblique. The clinician should suspect Brown’s syndrome when there is a V pattern <strong>of</strong> movement<br />
in the presence <strong>of</strong> apparent underacting inferior obliques<br />
40








![SISTEM SENSORY [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/20667975/1/190x245/sistem-sensory-compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)