Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
Strabismus - Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
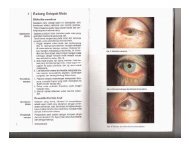
CONCEPTS IN STRABISMUS<br />
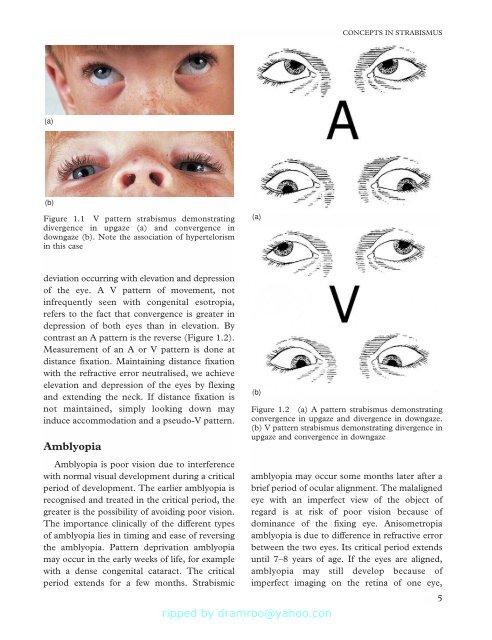
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
Figure 1.1 V pattern strabismus demonstrating<br />
divergence in upgaze (a) and convergence in<br />
downgaze (b). Note the association <strong>of</strong> hypertelorism<br />
in this case<br />
(a)<br />
deviation occurring with elevation and depression<br />
<strong>of</strong> the eye. A V pattern <strong>of</strong> movement, not<br />
infrequently seen with congenital esotropia,<br />
refers to the fact that convergence is greater in<br />
depression <strong>of</strong> both eyes than in elevation. By<br />
contrast an A pattern is the reverse (Figure 1.2).<br />
Measurement <strong>of</strong> an A or V pattern is done at<br />
distance fixation. Maintaining distance fixation<br />
with the refractive error neutralised, we achieve<br />
elevation and depression <strong>of</strong> the eyes by flexing<br />
and extending the neck. If distance fixation is<br />
not maintained, simply looking down may<br />
induce accommodation and a pseudo-V pattern.<br />
Amblyopia<br />
Amblyopia is poor vision due to interference<br />
with normal visual development during a critical<br />
period <strong>of</strong> development. The earlier amblyopia is<br />
recognised and treated in the critical period, the<br />
greater is the possibility <strong>of</strong> avoiding poor vision.<br />
The importance clinically <strong>of</strong> the different types<br />
<strong>of</strong> amblyopia lies in timing and ease <strong>of</strong> reversing<br />
the amblyopia. Pattern deprivation amblyopia<br />
may occur in the early weeks <strong>of</strong> life, for example<br />
with a dense congenital cataract. The critical<br />
period extends for a few months. Strabismic<br />
(b)<br />
Figure 1.2 (a) A pattern strabismus demonstrating<br />
convergence in upgaze and divergence in downgaze.<br />
(b) V pattern strabismus demonstrating divergence in<br />
upgaze and convergence in downgaze<br />
amblyopia may occur some months later after a<br />
brief period <strong>of</strong> ocular alignment. The malaligned<br />
eye with an imperfect view <strong>of</strong> the object <strong>of</strong><br />
regard is at risk <strong>of</strong> poor vision because <strong>of</strong><br />
dominance <strong>of</strong> the fixing eye. Anisometropia<br />
amblyopia is due to difference in refractive error<br />
between the two eyes. Its critical period extends<br />
until 7–8 years <strong>of</strong> age. If the eyes are aligned,<br />
amblyopia may still develop because <strong>of</strong><br />
imperfect imaging on the retina <strong>of</strong> one eye,<br />
5







![SISTEM SENSORY [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/20667975/1/190x245/sistem-sensory-compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)