CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
S<br />
Macroscopic Microscopic Dual level<br />
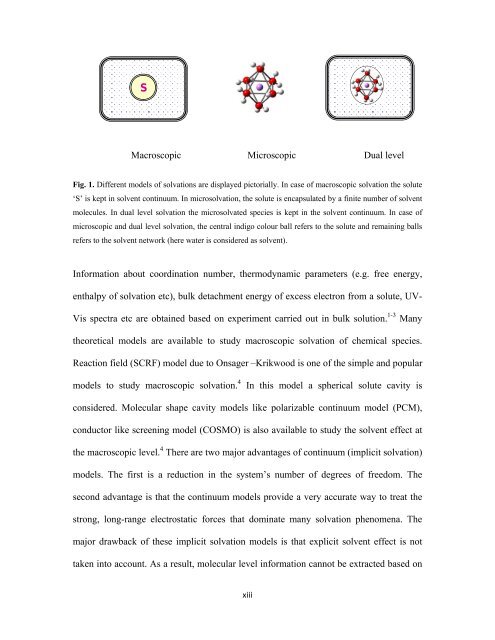
Fig. 1. Different models of solvations are displayed pictorially. In case of macroscopic solvation the solute<br />
‘S’ is kept in solvent continuum. In microsolvation, the solute is encapsulated by a finite number of solvent<br />
molecules. In dual level solvation the microsolvated species is kept in the solvent continuum. In case of<br />
microscopic and dual level solvation, the central indigo colour ball refers to the solute and remaining balls<br />
refers to the solvent network (here water is considered as solvent).<br />
Information about coordination number, thermodynamic parameters (e.g. free energy,<br />
enthalpy of solvation etc), bulk detachment energy of excess electron from a solute, UV-<br />
Vis spectra etc are obtained based on experiment carried out in bulk solution. 1-3 Many<br />
theoretical models are available to study macroscopic solvation of chemical species.<br />
Reaction field (SCRF) model due to Onsager –Krikwood is one of the simple and popular<br />
models to study macroscopic solvation. 4<br />
In this model a spherical solute cavity is<br />
considered. Molecular shape cavity models like polarizable continuum model (PCM),<br />
conductor like screening model (COSMO) is also available to study the solvent effect at<br />
the macroscopic level. 4 There are two major advantages of continuum (implicit solvation)<br />
models. The first is a reduction in the system’s number of degrees of freedom. The<br />
second advantage is that the continuum models provide a very accurate way to treat the<br />
strong, long-range electrostatic forces that dominate many solvation phenomena. The<br />
major drawback of these implicit solvation models is that explicit solvent effect is not<br />
taken into account. As a result, molecular level information cannot be extracted based on<br />
xiii