CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
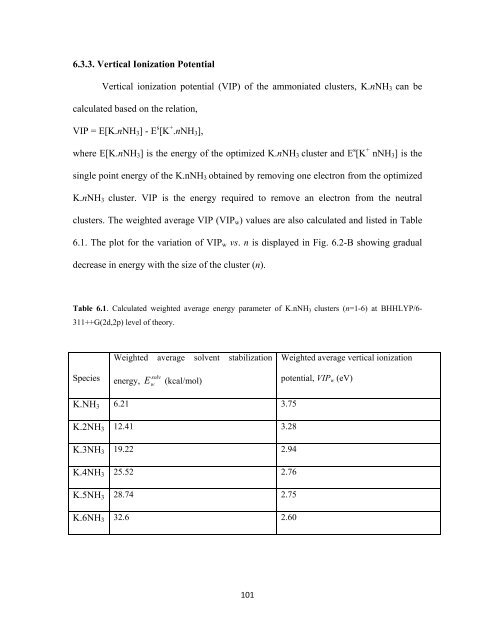
6.3.3. Vertical Ionization Potential<br />
Vertical ionization potential (VIP) of the ammoniated clusters, K.nNH 3 can be<br />
calculated based on the relation,<br />
VIP = E[K.nNH 3 ] - E s [K + .nNH 3 ],<br />
where E[K.nNH 3 ] is the energy of the optimized K.nNH 3 cluster and E s [K + nNH 3 ] is the<br />
single point energy of the K.nNH 3 obtained by removing one electron from the optimized<br />
K.nNH 3 cluster. VIP is the energy required to remove an electron from the neutral<br />
clusters. The weighted average VIP (VIP w ) values are also calculated and listed in Table<br />
6.1. The plot for the variation of VIP w vs. n is displayed in Fig. 6.2-B showing gradual<br />
decrease in energy with the size of the cluster (n).<br />
Table 6.1. Calculated weighted average energy parameter of K.nNH 3 clusters (n=1-6) at BHHLYP/6-<br />
311++G(2d,2p) level of theory.<br />
Species<br />
Weighted average solvent stabilization<br />
energy, E w solv (kcal/mol)<br />
Weighted average vertical ionization<br />
potential, VIP w (eV)<br />
K.NH 3 6.21 3.75<br />
K.2NH 3 12.41 3.28<br />
K.3NH 3 19.22 2.94<br />
K.4NH 3 25.52 2.76<br />
K.5NH 3 28.74 2.75<br />
K.6NH 3 32.6 2.60<br />
101