CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
CHEM01200604005 A. K. Pathak - Homi Bhabha National Institute
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
statistical average over all solvent degrees of freedom at thermal equilibrium. This field is<br />
usually called the reaction field in the regions of space occupied by the solute, since it is<br />
derived from the reaction of the solvent to the presence of the solute. On the other hand,<br />
the model used to study solvation process at molecular level is known as microsolvation<br />
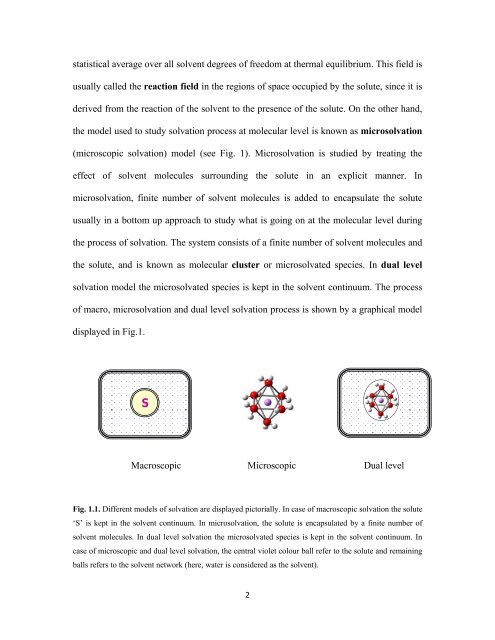
(microscopic solvation) model (see Fig. 1). Microsolvation is studied by treating the<br />
effect of solvent molecules surrounding the solute in an explicit manner. In<br />
microsolvation, finite number of solvent molecules is added to encapsulate the solute<br />
usually in a bottom up approach to study what is going on at the molecular level during<br />
the process of solvation. The system consists of a finite number of solvent molecules and<br />
the solute, and is known as molecular cluster or microsolvated species. In dual level<br />
solvation model the microsolvated species is kept in the solvent continuum. The process<br />
of macro, microsolvation and dual level solvation process is shown by a graphical model<br />
displayed in Fig.1.<br />
S<br />
Macroscopic Microscopic Dual level<br />
Fig. 1.1. Different models of solvation are displayed pictorially. In case of macroscopic solvation the solute<br />
‘S’ is kept in the solvent continuum. In microsolvation, the solute is encapsulated by a finite number of<br />
solvent molecules. In dual level solvation the microsolvated species is kept in the solvent continuum. In<br />
case of microscopic and dual level solvation, the central violet colour ball refer to the solute and remaining<br />
balls refers to the solvent network (here, water is considered as the solvent).<br />
2