POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA
POLITECHNIKA WARSZAWSKA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
5. Speed estimation of induction motor<br />
5.3. ANN based speed estimators<br />
5.3.1. Speed estimators with on-line ANN<br />
In this part of the thesis three methods based on an on-line ANN is presented. The<br />
first approach has been originally published by Ben-Brahim and Kurosawa [130] and<br />
is based on two flux models. The second method is a small modification of the first<br />
one, but with big improvement in the length of the learning time.<br />
The third method is the new method originally invented by the author, and is<br />
based on stator current calculations.<br />
5.3.1.1. Method based on two flux models<br />
The concept proposed in [130] is based on two independent rotor flux simulators<br />
[12]:<br />
- voltage model<br />
TN(dΨru/dt) = (xr/xM)[us - rs is - σxs TN(dis/dt)] (5.16)<br />
- current model<br />
TN(dΨri/dt) = [-(TN/Tr) + jωm]Ψri + (TN xM/Tr) is (5.17)<br />
where:<br />
Tr = (TN xr/rr) — rotor time constant,<br />
TN = (1/2πFSN) = (1/ 2π50 Hz) — nominal time constant,<br />
σ = 1- (xMxM/xrxs) — leakage factor.<br />
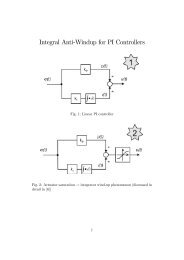
The block diagram of the NN speed estimator is shown in Fig.5.10.<br />
113















![[TCP] Opis układu - Instytut Sterowania i Elektroniki Przemysłowej ...](https://img.yumpu.com/23535443/1/184x260/tcp-opis-ukladu-instytut-sterowania-i-elektroniki-przemyslowej-.jpg?quality=85)