F-22 Plus-Up Environmental Assessment - Joint Base Elmendorf ...
F-22 Plus-Up Environmental Assessment - Joint Base Elmendorf ...
F-22 Plus-Up Environmental Assessment - Joint Base Elmendorf ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
F-<strong>22</strong> <strong>Plus</strong>-<strong>Up</strong> <strong>Environmental</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong><br />
2.0 Description of the Proposed Action and Alternatives<br />
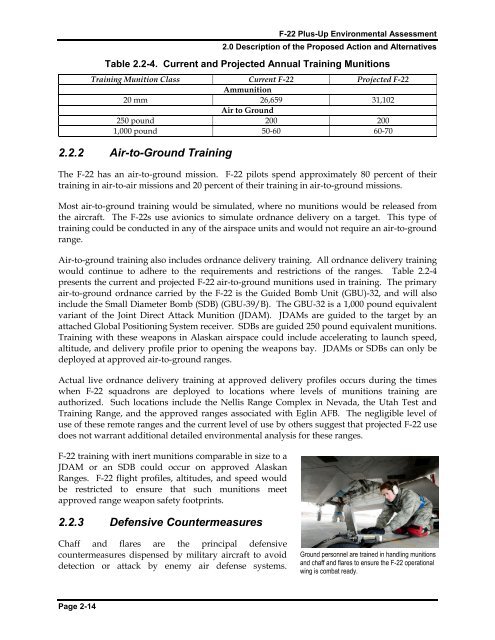
Table 2.2-4. Current and Projected Annual Training Munitions<br />
Training Munition Class Current F-<strong>22</strong> Projected F-<strong>22</strong><br />
Ammunition<br />
20 mm 26,659 31,102<br />
Air to Ground<br />
250 pound 200 200<br />
1,000 pound 50-60 60-70<br />
2.2.2 Air-to-Ground Training<br />
The F-<strong>22</strong> has an air-to-ground mission. F-<strong>22</strong> pilots spend approximately 80 percent of their<br />
training in air-to-air missions and 20 percent of their training in air-to-ground missions.<br />
Most air-to-ground training would be simulated, where no munitions would be released from<br />
the aircraft. The F-<strong>22</strong>s use avionics to simulate ordnance delivery on a target. This type of<br />
training could be conducted in any of the airspace units and would not require an air-to-ground<br />
range.<br />
Air-to-ground training also includes ordnance delivery training. All ordnance delivery training<br />
would continue to adhere to the requirements and restrictions of the ranges. Table 2.2-4<br />
presents the current and projected F-<strong>22</strong> air-to-ground munitions used in training. The primary<br />
air-to-ground ordnance carried by the F-<strong>22</strong> is the Guided Bomb Unit (GBU)-32, and will also<br />
include the Small Diameter Bomb (SDB) (GBU-39/B). The GBU-32 is a 1,000 pound equivalent<br />
variant of the <strong>Joint</strong> Direct Attack Munition (JDAM). JDAMs are guided to the target by an<br />
attached Global Positioning System receiver. SDBs are guided 250 pound equivalent munitions.<br />
Training with these weapons in Alaskan airspace could include accelerating to launch speed,<br />
altitude, and delivery profile prior to opening the weapons bay. JDAMs or SDBs can only be<br />
deployed at approved air-to-ground ranges.<br />
Actual live ordnance delivery training at approved delivery profiles occurs during the times<br />
when F-<strong>22</strong> squadrons are deployed to locations where levels of munitions training are<br />
authorized. Such locations include the Nellis Range Complex in Nevada, the Utah Test and<br />
Training Range, and the approved ranges associated with Eglin AFB. The negligible level of<br />
use of these remote ranges and the current level of use by others suggest that projected F-<strong>22</strong> use<br />
does not warrant additional detailed environmental analysis for these ranges.<br />
F-<strong>22</strong> training with inert munitions comparable in size to a<br />
JDAM or an SDB could occur on approved Alaskan<br />
Ranges. F-<strong>22</strong> flight profiles, altitudes, and speed would<br />
be restricted to ensure that such munitions meet<br />
approved range weapon safety footprints.<br />
2.2.3 Defensive Countermeasures<br />
Chaff and flares are the principal defensive<br />
countermeasures dispensed by military aircraft to avoid<br />
detection or attack by enemy air defense systems.<br />
Ground personnel are trained in handling munitions<br />
and chaff and flares to ensure the F-<strong>22</strong> operational<br />
wing is combat ready.<br />
Page 2-14