TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
lost packet at the receiver. Consequently, a particular Access Unit can be restored. Failures in the<br />
decoding process are rather distributed toward the less important objects, and then UEP reduces<br />
the effects of spatial and temporal errors propagation. This observation is shown in Figure 4-21<br />
where the decoded object ratio of configuration A is always better than configuration B.<br />
In this scenario, we setup two networks configurations to demonstrate the effect of the crosslayer<br />
system. For this reason, we mark each packet according to its priority score and we study the<br />
effect of this marking. We transmit the protected MPEG-4 scene over <strong>IP</strong> Best Effort network<br />
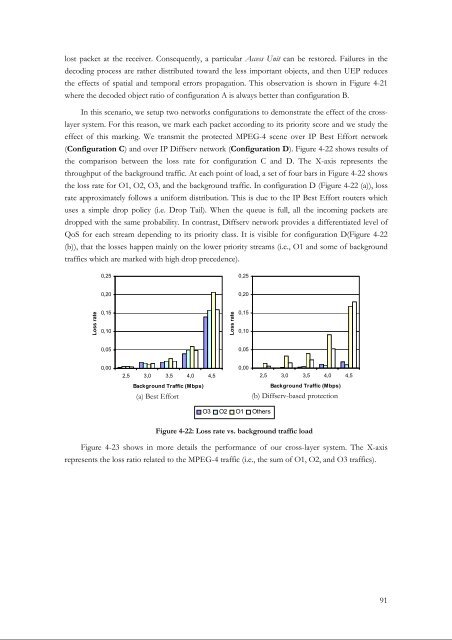
(Configuration C) and over <strong>IP</strong> Diffserv network (Configuration D). Figure 4-22 shows results of<br />
the comparison between the loss rate for configuration C and D. The X-axis represents the<br />
throughput of the background traffic. At each point of load, a set of four bars in Figure 4-22 shows<br />
the loss rate for O1, O2, O3, and the background traffic. In configuration D (Figure 4-22 (a)), loss<br />
rate approximately follows a uniform distribution. This is due to the <strong>IP</strong> Best Effort routers which<br />
uses a simple drop policy (i.e. Drop Tail). When the queue is full, all the incoming packets are<br />
dropped with the same probability. In contrast, Diffserv network provides a differentiated level of<br />
QoS for each stream depending to its priority class. It is visible for configuration D(Figure 4-22<br />
(b)), that the losses happen mainly on the lower priority streams (i.e., O1 and some of background<br />
traffics which are marked with high drop precedence).<br />
0,25<br />
0,25<br />
0,20<br />
0,20<br />
Loss rate<br />
0,15<br />
0,10<br />
Loss rate<br />
0,15<br />
0,10<br />
0,05<br />
0,05<br />
0,00<br />
0,00<br />
2,5 3,0 3,5 4,0 4,5<br />
2,5 3,0 3,5 4,0 4,5<br />
Background Traffic (Mbps)<br />
Background Traffic (Mbps)<br />
(a) Best Effort<br />
(b) Diffserv-based protection<br />
O3 O2 O1 Others<br />
Figure 4-22: Loss rate vs. background traffic load<br />
Figure 4-23 shows in more details the performance of our cross-layer system. The X-axis<br />
represents the loss ratio related to the MPEG-4 traffic (i.e., the sum of O1, O2, and O3 traffics).<br />
91