TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
educe the variability of the traffic and bandwidth requirement of the video stream, smoothing<br />
technique is necessary. Smoothing makes use of a client side buffer to receive data in advance of<br />
playback [91], [92], [93], [94], and [95].<br />
3.2.2 Loss and Error Management<br />
<strong>Packet</strong> loss is a problem that affects considerably the quality of the received video at the client.<br />
It can have a very destructive effect of the reconstructed video because of frame dependency.<br />
<strong>Packet</strong> loss may arrive at different level and under different consideration. In wired packet<br />
networks, the congestion is the first circumstance on packet loss. Entire packet can be discarded by<br />
routers. Whereas in wireless networks, the transmission channel may cause bit error. Thus, the<br />
packet could be rejected by the application layer.<br />
Before presenting the approaches for reliable video streaming, it is necessary to understand the<br />
effect of packet loss on compressed video stream. In general, there are two basic problems induced<br />
by video packet losses. First, the loss of bitstream synchronization or when important<br />
synchronization marker is lost. In this case, the decoder may loss track of what bits correspond to<br />
what parameters. Second, since the video has a particular structure composed of frames mutually<br />
dependent, the loss of one frame may make all depending frame unusable.<br />
To deal with the effect of losses, it is necessary to have functions to muffle the loss. There are<br />
two types of approaches for reliable video transmission. The first approach is a sender-based<br />
approach, in which the sender can be active or passive to recover from losses. The second<br />
approach is a receiver-based approach in which the client conceals the loss by some techniques.<br />
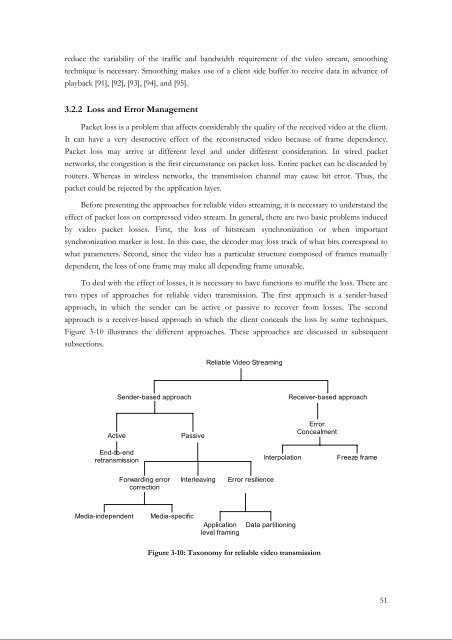
Figure 3-10 illustrates the different approaches. These approaches are discussed in subsequent<br />
subsections.<br />
Reliable <strong>Video</strong> <strong>Streaming</strong><br />
Sender-based approach<br />
Receiver-based approach<br />
Active<br />
Passive<br />
Error<br />
Concealment<br />
End-to-end<br />
retransmission<br />
Interpolation<br />
Freeze frame<br />
Forwarding error<br />
correction<br />
Interleaving<br />
Error resilience<br />
Media-independent<br />
Media-specific<br />
Application<br />
level framing<br />
Data partitioning<br />
Figure 3-10: Taxonomy for reliable video transmission<br />
51