TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
TITRE Adaptive Packet Video Streaming Over IP Networks - LaBRI
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
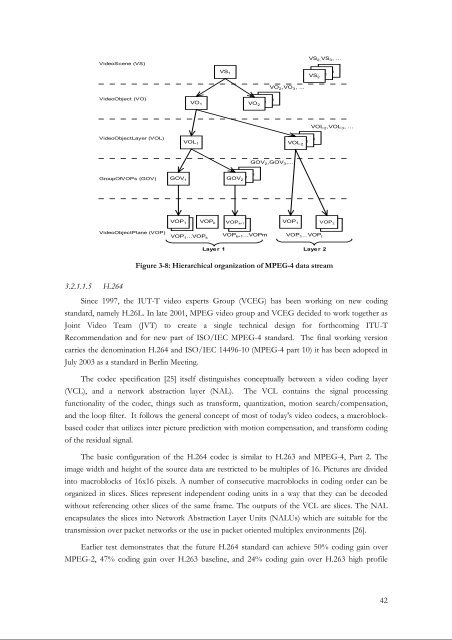
<strong>Video</strong>Scene (VS)<br />
<strong>Video</strong>Object (VO)<br />
<strong>Video</strong>ObjectLayer (VOL)<br />
GroupOfVOPs (GOV)<br />
<strong>Video</strong>ObjectPlane (VOP)<br />
VS 2, VS 3 , ...<br />
VS 1<br />
VS VS1 1<br />
VS2<br />
VOP<br />
VS 1 1<br />
VOP k VOP<br />
VS k+1<br />
1<br />
VOP 1 VOP<br />
VS 2<br />
1<br />
VO 1<br />
VS VS1 1<br />
VO2<br />
VO 2 ,VO 3 , ...<br />
VOL 1<br />
VS VS1 1<br />
VOL2<br />
VOL 2 ,VOL 3 , ...<br />
GOV 1<br />
VS VS1 1<br />
GOV2<br />
GOV 2 ,GOV 3 ,...<br />
VOP 1 ...VOP k<br />
VOP k+1 ...VOPm<br />
VOP 1 ...VOP t<br />
Layer 1 Layer 2<br />
Figure 3-8: Hierarchical organization of MPEG-4 data stream<br />
3.2.1.1.5 H.264<br />
Since 1997, the IUT-T video experts Group (VCEG) has been working on new coding<br />
standard, namely H.26L. In late 2001, MPEG video group and VCEG decided to work together as<br />
Joint <strong>Video</strong> Team (JVT) to create a single technical design for forthcoming ITU-T<br />
Recommendation and for new part of ISO/IEC MPEG-4 standard. The final working version<br />
carries the denomination H.264 and ISO/IEC 14496-10 (MPEG-4 part 10) it has been adopted in<br />
July 2003 as a standard in Berlin Meeting.<br />
The codec specification [25] itself distinguishes conceptually between a video coding layer<br />
(VCL), and a network abstraction layer (NAL). The VCL contains the signal processing<br />
functionality of the codec, things such as transform, quantization, motion search/compensation,<br />
and the loop filter. It follows the general concept of most of today's video codecs, a macroblockbased<br />
coder that utilizes inter picture prediction with motion compensation, and transform coding<br />
of the residual signal.<br />
The basic configuration of the H.264 codec is similar to H.263 and MPEG-4, Part 2. The<br />
image width and height of the source data are restricted to be multiples of 16. Pictures are divided<br />
into macroblocks of 16x16 pixels. A number of consecutive macroblocks in coding order can be<br />
organized in slices. Slices represent independent coding units in a way that they can be decoded<br />
without referencing other slices of the same frame. The outputs of the VCL are slices. The NAL<br />
encapsulates the slices into Network Abstraction Layer Units (NALUs) which are suitable for the<br />
transmission over packet networks or the use in packet oriented multiplex environments [26].<br />
Earlier test demonstrates that the future H.264 standard can achieve 50% coding gain over<br />
MPEG-2, 47% coding gain over H.263 baseline, and 24% coding gain over H.263 high profile<br />
42