Landcom Book 4 Maintenance - WSUD
Landcom Book 4 Maintenance - WSUD
Landcom Book 4 Maintenance - WSUD
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Water Sensitive Urban Design<br />
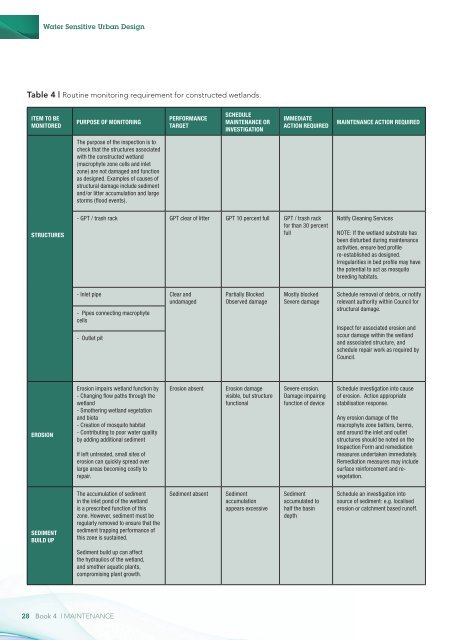
Table 4 | Routine monitoring requirement for constructed wetlands.<br />
Item to be<br />
Monitored<br />
Purpose of Monitoring<br />
Performance<br />
Target<br />
Schedule<br />
<strong>Maintenance</strong> or<br />
Investigation<br />
Immediate<br />
Action Required<br />
<strong>Maintenance</strong> Action Required<br />
The purpose of the inspection is to<br />
check that the structures associated<br />
with the constructed wetland<br />
(macrophyte zone cells and inlet<br />
zone) are not damaged and function<br />
as designed. Examples of causes of<br />
structural damage include sediment<br />
and/or litter accumulation and large<br />
storms (flood events).<br />
Structures<br />
- GPT / trash rack GPT clear of litter GPT 10 percent full GPT / trash rack<br />
for than 30 percent<br />
full<br />
Notify Cleaning Services<br />
NOTE: If the wetland substrate has<br />
been disturbed during maintenance<br />
activities, ensure bed profile<br />
re-established as designed.<br />
Irregularities in bed profile may have<br />
the potential to act as mosquito<br />
breeding habitats.<br />
- Inlet pipe Clear and<br />
undamaged<br />
- Pipes connecting macrophyte<br />
cells<br />
- Outlet pit<br />
Partially Blocked<br />
Observed damage<br />
Mostly blocked<br />
Severe damage<br />
Schedule removal of debris, or notify<br />
relevant authority within Council for<br />
structural damage.<br />
Inspect for associated erosion and<br />
scour damage within the wetland<br />
and associated structure, and<br />
schedule repair work as required by<br />
Council.<br />
Erosion<br />
Erosion impairs wetland function by<br />
- Changing flow paths through the<br />
wetland<br />
- Smothering wetland vegetation<br />
and biota<br />
- Creation of mosquito habitat<br />
- Contributing to poor water quality<br />
by adding additional sediment<br />
If left untreated, small sites of<br />
erosion can quickly spread over<br />
large areas becoming costly to<br />
repair.<br />
Erosion absent<br />
Erosion damage<br />
visible, but structure<br />
functional<br />
Severe erosion.<br />
Damage impairing<br />
function of device<br />
Schedule investigation into cause<br />
of erosion. Action appropriate<br />
stabilisation response.<br />
Any erosion damage of the<br />
macrophyte zone batters, berms,<br />
and around the inlet and outlet<br />
structures should be noted on the<br />
Inspection Form and remediation<br />
measures undertaken immediately.<br />
Remediation measures may include<br />
surface reinforcement and revegetation.<br />
Sediment<br />
build up<br />
The accumulation of sediment<br />
in the inlet pond of the wetland<br />
is a prescribed function of this<br />
zone. However, sediment must be<br />
regularly removed to ensure that the<br />
sediment trapping performance of<br />
this zone is sustained.<br />
Sediment absent<br />
Sediment<br />
accumulation<br />
appears excessive<br />
Sediment<br />
accumulated to<br />
half the basin<br />
depth<br />
Schedule an investigation into<br />
source of sediment: e.g. localised<br />
erosion or catchment based runoff.<br />
Sediment build up can affect<br />
the hydraulics of the wetland,<br />
and smother aquatic plants,<br />
compromising plant growth.<br />
28 <strong>Book</strong> 4 | MAINTENANCE