Landcom Book 4 Maintenance - WSUD
Landcom Book 4 Maintenance - WSUD
Landcom Book 4 Maintenance - WSUD
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Water Sensitive Urban Design<br />
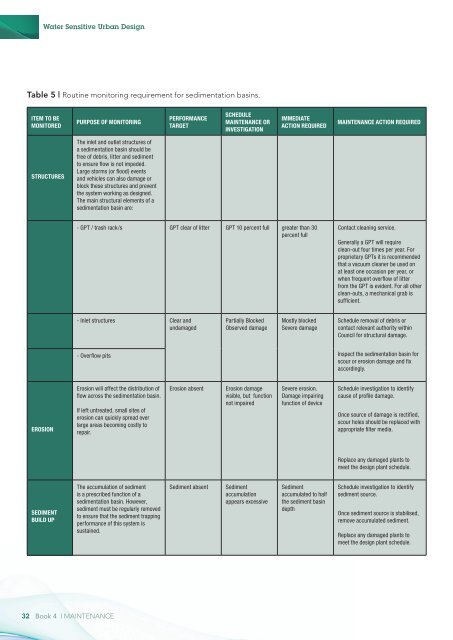
Table 5 | Routine monitoring requirement for sedimentation basins.<br />
Item to be<br />
Monitored<br />
Purpose of Monitoring<br />
Performance<br />
Target<br />
Schedule<br />
<strong>Maintenance</strong> or<br />
Investigation<br />
Immediate<br />
Action Required<br />
<strong>Maintenance</strong> Action Required<br />
Structures<br />
The inlet and outlet structures of<br />
a sedimentation basin should be<br />
free of debris, litter and sediment<br />
to ensure flow is not impeded.<br />
Large storms (or flood) events<br />
and vehicles can also damage or<br />
block these structures and prevent<br />
the system working as designed.<br />
The main structural elements of a<br />
sedimentation basin are:<br />
- GPT / trash rack/s GPT clear of litter GPT 10 percent full greater than 30<br />
percent full<br />
Contact cleaning service.<br />
Generally a GPT will require<br />
clean-out four times per year. For<br />
proprietary GPTs it is recommended<br />
that a vacuum cleaner be used on<br />
at least one occasion per year, or<br />
when frequent overflow of litter<br />
from the GPT is evident. For all other<br />
clean-outs, a mechanical grab is<br />
sufficient.<br />
- Inlet structures Clear and<br />
undamaged<br />
Partially Blocked<br />
Observed damage<br />
Mostly blocked<br />
Severe damage<br />
Schedule removal of debris or<br />
contact relevant authority within<br />
Council for structural damage.<br />
- Overflow pits<br />
Inspect the sedimentation basin for<br />
scour or erosion damage and fix<br />
accordingly.<br />
Erosion<br />
Erosion will affect the distribution of<br />
flow across the sedimentation basin.<br />
If left untreated, small sites of<br />
erosion can quickly spread over<br />
large areas becoming costly to<br />
repair.<br />
Erosion absent<br />
Erosion damage<br />
visible, but function<br />
not impaired<br />
Severe erosion.<br />
Damage impairing<br />
function of device<br />
Schedule investigation to identify<br />
cause of profile damage.<br />
Once source of damage is rectified,<br />
scour holes should be replaced with<br />
appropriate filter media.<br />
Replace any damaged plants to<br />
meet the design plant schedule.<br />
Sediment<br />
build up<br />
The accumulation of sediment<br />
is a prescribed function of a<br />
sedimentation basin. However,<br />
sediment must be regularly removed<br />
to ensure that the sediment trapping<br />
performance of this system is<br />
sustained.<br />
Sediment absent<br />
Sediment<br />
accumulation<br />
appears excessive<br />
Sediment<br />
accumulated to half<br />
the sediment basin<br />
depth<br />
Schedule investigation to identify<br />
sediment source.<br />
Once sediment source is stabilised,<br />
remove accumulated sediment.<br />
Replace any damaged plants to<br />
meet the design plant schedule.<br />
32 <strong>Book</strong> 4 | MAINTENANCE