You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
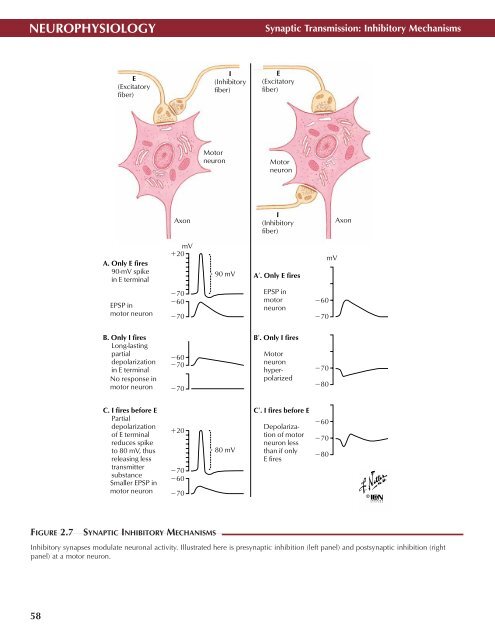
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
Synaptic Transmission: Inhibitory Mechanisms<br />
E<br />
(Excitatory<br />
fiber)<br />
I<br />
(Inhibitory<br />
fiber)<br />
E<br />
(Excitatory<br />
fiber)<br />
Motor<br />
neuron<br />
Motor<br />
neuron<br />
Axon<br />
I<br />
(Inhibitory<br />
fiber)<br />
Axon<br />
A. Only E fires<br />
90-mV spike<br />
in E terminal<br />
mV<br />
20<br />
90 mV A′. Only E fires<br />
mV<br />
EPSP in<br />
motor neuron<br />
70<br />
60<br />
70<br />
EPSP in<br />
motor<br />
neuron<br />
60<br />
70<br />
B. Only I fires<br />
Long-lasting<br />
partial<br />
depolarization<br />
in E terminal<br />
No response in<br />
motor neuron<br />
60<br />
70<br />
70<br />
B′. Only I fires<br />
Motor<br />
neuron<br />
hyperpolarized<br />
70<br />
80<br />
C. I fires before E<br />
Partial<br />
depolarization<br />
of E terminal<br />
reduces spike<br />
to 80 mV, thus<br />
releasing less<br />
transmitter<br />
substance<br />
Smaller EPSP in<br />
motor neuron<br />
20<br />
70<br />
60<br />
70<br />
80 mV<br />
C′. I fires before E<br />
Depolarization<br />
of motor<br />
neuron less<br />
than if only<br />
E fires<br />
60<br />
70<br />
80<br />
©<br />
FIGURE 2.7<br />
SYNAPTIC INHIBITORY MECHANISMS •<br />
Inhibitory synapses modulate neuronal activity. Illustrated here is presynaptic inhibition (left panel) and postsynaptic inhibition (right<br />
panel) at a motor neuron.<br />
58