You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
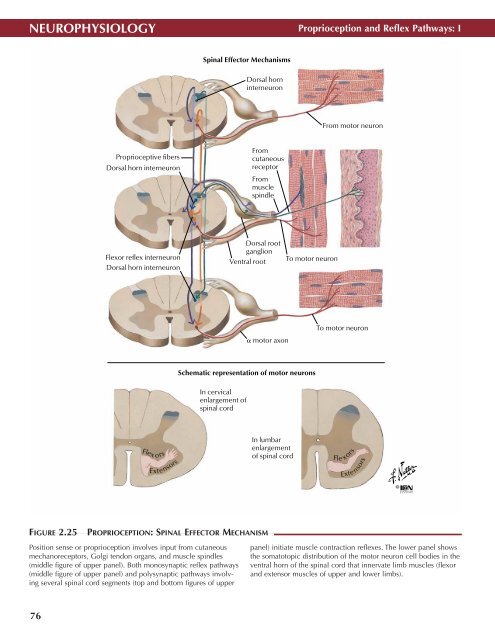
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
Proprioception and Reflex Pathways: I<br />
Spinal Effector Mechanisms<br />
Dorsal horn<br />
interneuron<br />
From motor neuron<br />
Proprioceptive fibers<br />
Dorsal horn interneuron<br />
From<br />
cutaneous<br />
receptor<br />
From<br />
muscle<br />
spindle<br />
Flexor reflex interneuron<br />
Dorsal horn interneuron<br />
Dorsal root<br />
ganglion<br />
Ventral root<br />
To motor neuron<br />
motor axon<br />
To motor neuron<br />
Schematic representation of motor neurons<br />
In cervical<br />
enlargement of<br />
spinal cord<br />
Flex ors<br />
Extensors<br />
In lumbar<br />
enlargement<br />
of spinal cord<br />
Fle<br />
xors<br />
Exte nsors<br />
©<br />
FIGURE 2.25<br />
PROPRIOCEPTION: SPINAL EFFECTOR MECHANISM •<br />
Position sense or proprioception involves input from cutaneous<br />
mechanoreceptors, Golgi tendon organs, and muscle spindles<br />
(middle figure of upper panel). Both monosynaptic reflex pathways<br />
(middle figure of upper panel) and polysynaptic pathways involving<br />
several spinal cord segments (top and bottom figures of upper<br />
panel) initiate muscle contraction reflexes. The lower panel shows<br />
the somatotopic distribution of the motor neuron cell bodies in the<br />
ventral horn of the spinal cord that innervate limb muscles (flexor<br />
and extensor muscles of upper and lower limbs).<br />
76