You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
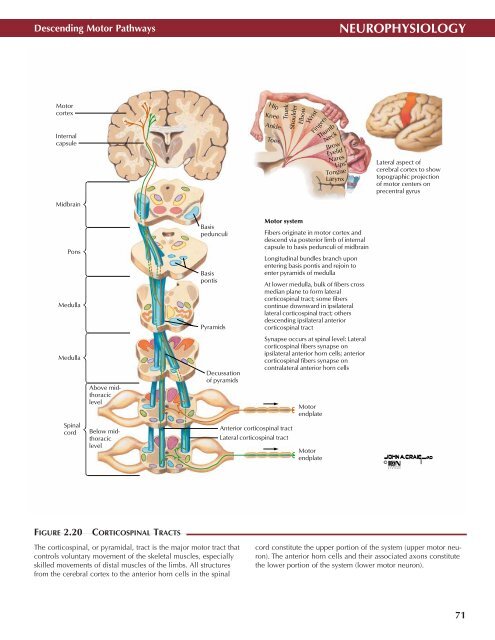
Descending Motor Pathways<br />
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
Motor<br />
cortex<br />
Internal<br />
capsule<br />
Hip<br />
Knee<br />
Ankle<br />
Toes<br />
Trunk<br />
Shoulder<br />
Elbow<br />
Wrist<br />
Fingers<br />
Thumb<br />
Neck<br />
Brow<br />
Eyelid<br />
Nares<br />
Lips<br />
Tongue<br />
Larynx<br />
Lateral aspect of<br />
cerebral cortex to show<br />
topographic projection<br />
of motor centers on<br />
precentral gyrus<br />
Midbrain<br />
Pons<br />
Medulla<br />
Basis<br />
pedunculi<br />
Basis<br />
pontis<br />
Pyramids<br />
Motor system<br />
Fibers originate in motor cortex and<br />
descend via posterior limb of internal<br />
capsule to basis pedunculi of midbrain<br />
Longitudinal bundles branch upon<br />
entering basis pontis and rejoin to<br />
enter pyramids of medulla<br />
At lower medulla, bulk of fibers cross<br />
median plane to form lateral<br />
corticospinal tract; some fibers<br />
continue downward in ipsilateral<br />
lateral corticospinal tract; others<br />
descending ipsilateral anterior<br />
corticospinal tract<br />
Medulla<br />
Above midthoracic<br />
level<br />
Decussation<br />
of pyramids<br />
Synapse occurs at spinal level: Lateral<br />
corticospinal fibers synapse on<br />
ipsilateral anterior horn cells; anterior<br />
corticospinal fibers synapse on<br />
contralateral anterior horn cells<br />
Motor<br />
endplate<br />
Spinal<br />
cord<br />
Below midthoracic<br />
level<br />
Anterior corticospinal tract<br />
Lateral corticospinal tract<br />
Motor<br />
endplate<br />
©<br />
FIGURE 2.20<br />
CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS •<br />
The corticospinal, or pyramidal, tract is the major motor tract that<br />
controls voluntary movement of the skeletal muscles, especially<br />
skilled movements of distal muscles of the limbs. All structures<br />
from the cerebral cortex to the anterior horn cells in the spinal<br />
cord constitute the upper portion of the system (upper motor neuron).<br />
The anterior horn cells and their associated axons constitute<br />
the lower portion of the system (lower motor neuron).<br />
71