Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
Vestibular System: Vestibulospinal Tracts<br />
Excitatory<br />
endings<br />
Inhibitory<br />
endings<br />
Ascending fibers in medial<br />
longitudinal fasciculi<br />
Superior<br />
Medial<br />
Lateral<br />
Inferior<br />
Vestibular nuclei<br />
Upper<br />
limb<br />
Rostral<br />
Trunk<br />
Ventral<br />
Dorsal<br />
To<br />
cerebellum<br />
Caudal<br />
Lower<br />
limb<br />
Somatotopical<br />
pattern in lateral<br />
vestibular nucleus<br />
Motor neuron<br />
(controlling<br />
neck muscles)<br />
Vestibular<br />
ganglion<br />
and<br />
nerve<br />
Medial vestibulospinal<br />
fibers in medial<br />
longitudinal fasciculi<br />
Lateral<br />
vestibulospinal<br />
tract<br />
Fibers from cristae<br />
(rotational stimuli)<br />
Excitatory<br />
endings<br />
to back<br />
muscles<br />
? ?<br />
Excitatory<br />
interneuron<br />
Inhibitory<br />
interneuron<br />
Fibers from maculae<br />
(gravitational stimuli)<br />
Lower<br />
part of<br />
cervical<br />
spinal cord<br />
To axial<br />
muscles<br />
Lumbar part of<br />
spinal cord<br />
?<br />
Inhibitory<br />
ending<br />
To flexor muscles<br />
To extensor muscles<br />
Inhibitory ending<br />
?<br />
To axial muscles<br />
Excitatory ending<br />
Lateral vestibulospinal tract<br />
Inhibitory interneuron<br />
Excitatory synapse<br />
To flexor muscles<br />
To extensor muscles<br />
©<br />
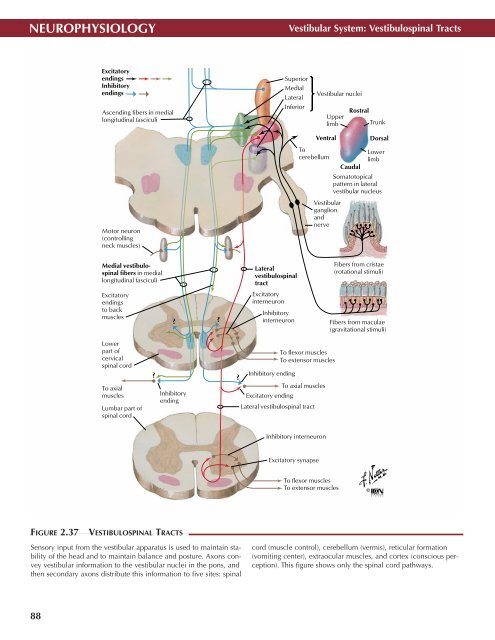
FIGURE 2.37<br />
VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACTS •<br />
Sensory input from the vestibular apparatus is used to maintain stability<br />
of the head and to maintain balance and posture. Axons convey<br />
vestibular information to the vestibular nuclei in the pons, and<br />
then secondary axons distribute this information to five sites: spinal<br />
cord (muscle control), cerebellum (vermis), reticular formation<br />
(vomiting center), extraocular muscles, and cortex (conscious perception).<br />
This figure shows only the spinal cord pathways.<br />
88