You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
Cutaneous Sensory Receptors<br />
Basal<br />
epithelial<br />
cells<br />
Hair follicle<br />
Free nerve endings<br />
Hair shaft<br />
Melanocyte<br />
Arrector muscle of hair<br />
Sebaceous gland<br />
Cuticle<br />
Internal sheath<br />
External sheath<br />
Glassy<br />
membrane<br />
Connective<br />
tissue layer<br />
Hair cuticle<br />
Sweat gland<br />
Hair matrix<br />
Papilla of hair follicle<br />
Pacinian<br />
corpuscle<br />
Artery<br />
Detail of Merkel’s disc<br />
Meissner’s corpuscle<br />
Pore of sweat gland<br />
Vein<br />
Sensory nerves<br />
Elastic fibers<br />
Skin ligaments<br />
(retinacula cutis)<br />
Motor<br />
(autonomic)<br />
nerve<br />
Desmosomes<br />
Cutaneous<br />
nerve<br />
Stratum corneum<br />
Stratum<br />
lucidum<br />
Stratum<br />
spinosum<br />
Dermal<br />
papilla<br />
(of papillary<br />
layer)<br />
Reticular<br />
layer<br />
Stratum<br />
granulosum<br />
Subcutaneous<br />
artery and vein<br />
Cross section<br />
Stratum<br />
basale<br />
Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue<br />
Basement membrane<br />
Axon terminal<br />
Mitochondrion<br />
Schwann cell<br />
Cytoplasmic<br />
protrusion<br />
Merkel<br />
cell<br />
Mitochondria<br />
Lobulated<br />
nucleus<br />
Expanded<br />
axon terminal<br />
Granulated<br />
vesicles<br />
Axon<br />
©<br />
Schwann<br />
cell<br />
Schwann cells<br />
Detail of free nerve ending<br />
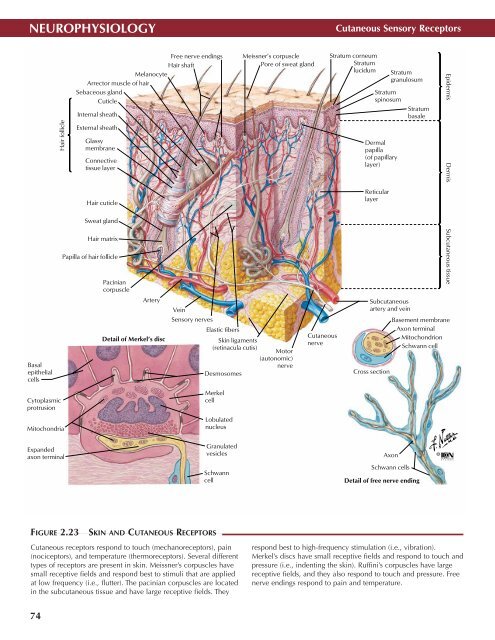
FIGURE 2.23<br />
SKIN AND CUTANEOUS RECEPTORS •<br />
Cutaneous receptors respond to touch (mechanoreceptors), pain<br />
(nociceptors), and temperature (thermoreceptors). Several different<br />
types of receptors are present in skin. Meissner’s corpuscles have<br />
small receptive fields and respond best to stimuli that are applied<br />
at low frequency (i.e., flutter). The pacinian corpuscles are located<br />
in the subcutaneous tissue and have large receptive fields. They<br />
respond best to high-frequency stimulation (i.e., vibration).<br />
Merkel’s discs have small receptive fields and respond to touch and<br />
pressure (i.e., indenting the skin). Ruffini’s corpuscles have large<br />
receptive fields, and they also respond to touch and pressure. Free<br />
nerve endings respond to pain and temperature.<br />
74