Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
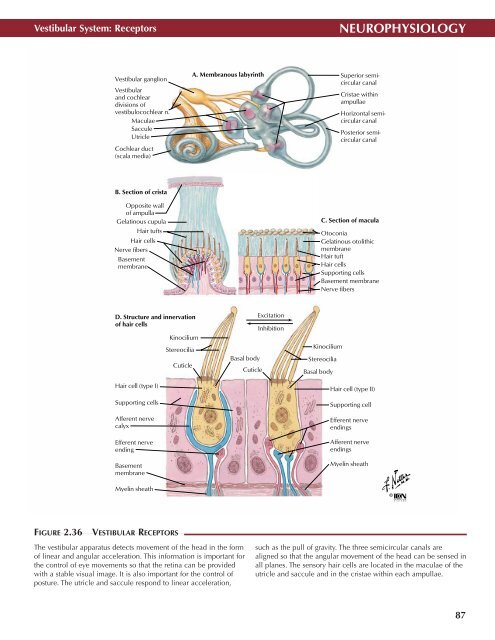
Vestibular System: Receptors<br />
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
Vestibular ganglion<br />
Vestibular<br />
and cochlear<br />
divisions of<br />
vestibulocochlear n.<br />
Maculae<br />
Saccule<br />
Utricle<br />
Cochlear duct<br />
(scala media)<br />
A. Membranous labyrinth<br />
Superior semicircular<br />
canal<br />
Cristae within<br />
ampullae<br />
Horizontal semicircular<br />
canal<br />
Posterior semicircular<br />
canal<br />
B. Section of crista<br />
Opposite wall<br />
of ampulla<br />
Gelatinous cupula<br />
Hair tufts<br />
Hair cells<br />
Nerve fibers<br />
Basement<br />
membrane<br />
C. Section of macula<br />
Otoconia<br />
Gelatinous otolithic<br />
membrane<br />
Hair tuft<br />
Hair cells<br />
Supporting cells<br />
Basement membrane<br />
Nerve fibers<br />
D. Structure and innervation<br />
of hair cells<br />
Hair cell (type I)<br />
Supporting cells<br />
Afferent nerve<br />
calyx<br />
Efferent nerve<br />
ending<br />
Basement<br />
membrane<br />
Kinocilium<br />
Stereocilia<br />
Cuticle<br />
Excitation<br />
Inhibition<br />
Basal body<br />
Cuticle<br />
Kinocilium<br />
Stereocilia<br />
Basal body<br />
Hair cell (type II)<br />
Supporting cell<br />
Efferent nerve<br />
endings<br />
Afferent nerve<br />
endings<br />
Myelin sheath<br />
Myelin sheath<br />
©<br />
FIGURE 2.36<br />
VESTIBULAR RECEPTORS •<br />
The vestibular apparatus detects movement of the head in the form<br />
of linear and angular acceleration. This information is important for<br />
the control of eye movements so that the retina can be provided<br />
with a stable visual image. It is also important for the control of<br />
posture. The utricle and saccule respond to linear acceleration,<br />
such as the pull of gravity. The three semicircular canals are<br />
aligned so that the angular movement of the head can be sensed in<br />
all planes. The sensory hair cells are located in the maculae of the<br />
utricle and saccule and in the cristae within each ampullae.<br />
87