Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Proprioception and Reflex Pathways: IV<br />
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
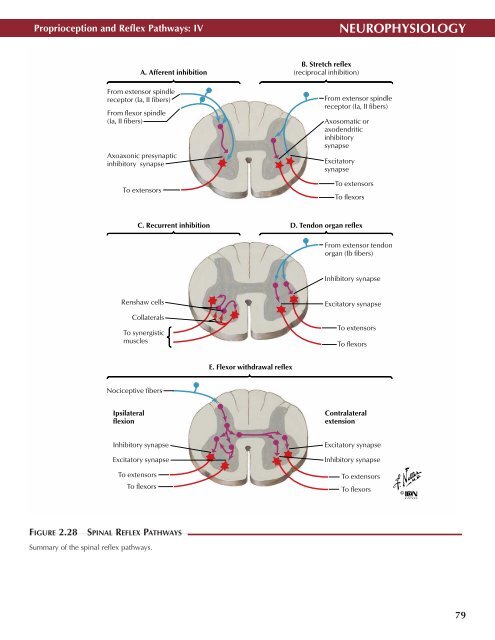
A. Afferent inhibition<br />
From extensor spindle<br />
receptor (Ia, II fibers)<br />
From flexor spindle<br />
(Ia, II fibers)<br />
Axoaxonic presynaptic<br />
inhibitory synapse<br />
To extensors<br />
B. Stretch reflex<br />
(reciprocal inhibition)<br />
From extensor spindle<br />
receptor (Ia, II fibers)<br />
Axosomatic or<br />
axodendritic<br />
inhibitory<br />
synapse<br />
Excitatory<br />
synapse<br />
To extensors<br />
To flexors<br />
C. Recurrent inhibition<br />
D. Tendon organ reflex<br />
From extensor tendon<br />
organ (Ib fibers)<br />
Inhibitory synapse<br />
Renshaw cells<br />
Collaterals<br />
To synergistic<br />
muscles<br />
Excitatory synapse<br />
To extensors<br />
To flexors<br />
E. Flexor withdrawal reflex<br />
Nociceptive fibers<br />
Ipsilateral<br />
flexion<br />
Contralateral<br />
extension<br />
Inhibitory synapse<br />
Excitatory synapse<br />
To extensors<br />
To flexors<br />
Excitatory synapse<br />
Inhibitory synapse<br />
To extensors<br />
To flexors<br />
©<br />
FIGURE 2.28<br />
SPINAL REFLEX PATHWAYS •<br />
Summary of the spinal reflex pathways.<br />
79