You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
Hypothalamus<br />
Lateral<br />
ventricle<br />
Septum<br />
pellucidum<br />
Fornix<br />
Corpus callosum<br />
Medial<br />
forebrain<br />
bundle<br />
Lateral<br />
preoptic<br />
nucleus<br />
Anterior<br />
commissure<br />
Medial<br />
preoptic<br />
nucleus<br />
From<br />
Thalamus<br />
hippocampal<br />
formation<br />
Interthalamic<br />
Lateral<br />
adhesion<br />
hypothalamic area<br />
Paraventricular nucleus<br />
Anterior hypothalamic area<br />
Dorsal hypothalamic area<br />
Dorsomedial nucleus<br />
Mamillothalamic tract<br />
Posterior area<br />
Periventricular<br />
nucleus<br />
Nucleus<br />
intercalatus<br />
Olfactory<br />
tract<br />
Optic (II)<br />
nerve<br />
Optic chiasm<br />
Anterior<br />
lobe of<br />
pituitary<br />
Fornix<br />
Ventromedial<br />
nucleus<br />
Mamillary<br />
complex<br />
Tuberohypophyseal tract<br />
Red nucleus<br />
Oculomotor (III) nerve<br />
Supraoptic nucleus<br />
Supraopticohypophyseal<br />
tract<br />
Posterior lobe of pituitary<br />
Cerebral<br />
peduncle<br />
Dorsal<br />
longitudinal<br />
fasciculus<br />
Descending<br />
hypothalamic<br />
connections<br />
Pons<br />
Reticular<br />
formation<br />
©<br />
CHART 2.3<br />
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS<br />
Hypothalamic Area<br />
Preoptic and anterior<br />
Posterior<br />
Lateral<br />
Ventromedial<br />
Supraoptic (subfornical organ and organum vasculosum)<br />
Paraventricular<br />
Periventricular<br />
*Stimulation of the center causes the responses listed.<br />
Major Functions*<br />
Heat loss center: cutaneous vasodilation and sweating<br />
Heat conservation center: cutaneous vasoconstriction and shivering<br />
Feeding center: eating behavior<br />
Satiety center: inhibits eating behavior<br />
ADH and oxytocin secretion (sensation of thirst)<br />
ADH and oxytocin secretion<br />
Releasing hormones for the anterior pituitary<br />
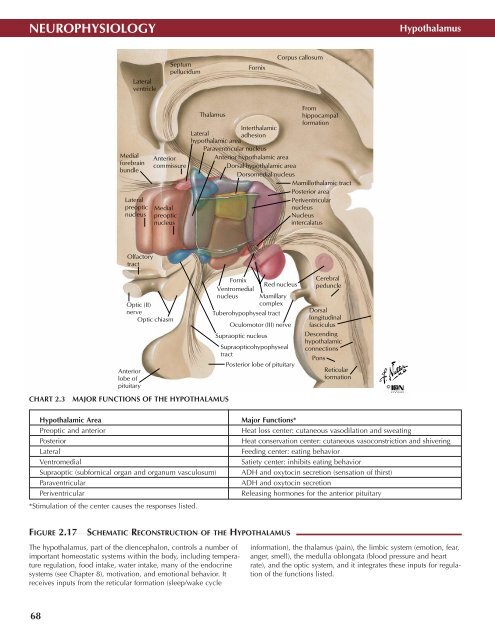
FIGURE 2.17<br />
SCHEMATIC RECONSTRUCTION OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS •<br />
The hypothalamus, part of the diencephalon, controls a number of<br />
important homeostatic systems within the body, including temperature<br />
regulation, food intake, water intake, many of the endocrine<br />
systems (see Chapter 8), motivation, and emotional behavior. It<br />
receives inputs from the reticular formation (sleep/wake cycle<br />
information), the thalamus (pain), the limbic system (emotion, fear,<br />
anger, smell), the medulla oblongata (blood pressure and heart<br />
rate), and the optic system, and it integrates these inputs for regulation<br />
of the functions listed.<br />
68