You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Proprioception and Reflex Pathways: II<br />
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY<br />
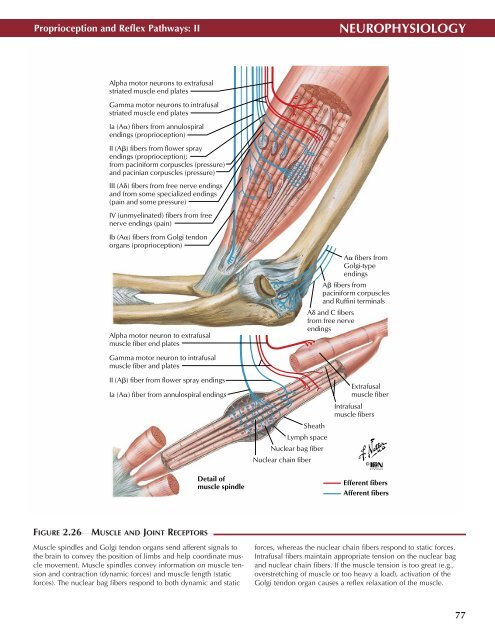
Alpha motor neurons to extrafusal<br />
striated muscle end plates<br />
Gamma motor neurons to intrafusal<br />
striated muscle end plates<br />
Ia (A) fibers from annulospiral<br />
endings (proprioception)<br />
II (A) fibers from flower spray<br />
endings (proprioception);<br />
from paciniform corpuscles (pressure)<br />
and pacinian corpuscles (pressure)<br />
III (A) fibers from free nerve endings<br />
and from some specialized endings<br />
(pain and some pressure)<br />
IV (unmyelinated) fibers from free<br />
nerve endings (pain)<br />
Ib (A) fibers from Golgi tendon<br />
organs (proprioception)<br />
Alpha motor neuron to extrafusal<br />
muscle fiber end plates<br />
A fibers from<br />
Golgi-type<br />
endings<br />
A fibers from<br />
paciniform corpuscles<br />
and Ruffini terminals<br />
A and C fibers<br />
from free nerve<br />
endings<br />
Gamma motor neuron to intrafusal<br />
muscle fiber and plates<br />
II (A) fiber from flower spray endings<br />
Ia (A) fiber from annulospiral endings<br />
Detail of<br />
muscle spindle<br />
Sheath<br />
Lymph space<br />
Nuclear bag fiber<br />
Nuclear chain fiber<br />
Extrafusal<br />
muscle fiber<br />
Intrafusal<br />
muscle fibers<br />
©<br />
Efferent fibers<br />
Afferent fibers<br />
FIGURE 2.26<br />
MUSCLE AND JOINT RECEPTORS •<br />
Muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs send afferent signals to<br />
the brain to convey the position of limbs and help coordinate muscle<br />
movement. Muscle spindles convey information on muscle tension<br />
and contraction (dynamic forces) and muscle length (static<br />
forces). The nuclear bag fibers respond to both dynamic and static<br />
forces, whereas the nuclear chain fibers respond to static forces.<br />
Intrafusal fibers maintain appropriate tension on the nuclear bag<br />
and nuclear chain fibers. If the muscle tension is too great (e.g.,<br />
overstretching of muscle or too heavy a load), activation of the<br />
Golgi tendon organ causes a reflex relaxation of the muscle.<br />
77