biologia - Studia
biologia - Studia
biologia - Studia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
V. MUNTEAN, C.-G. MAIER, R. CARPA, C. MUREŞAN, A. C. FARKAS<br />
100000<br />
10000<br />
Total coliforms/l<br />
1000<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
P1 P2 P3 P4 P5<br />
Sampling site<br />
Spring Summer Autumn Winter<br />
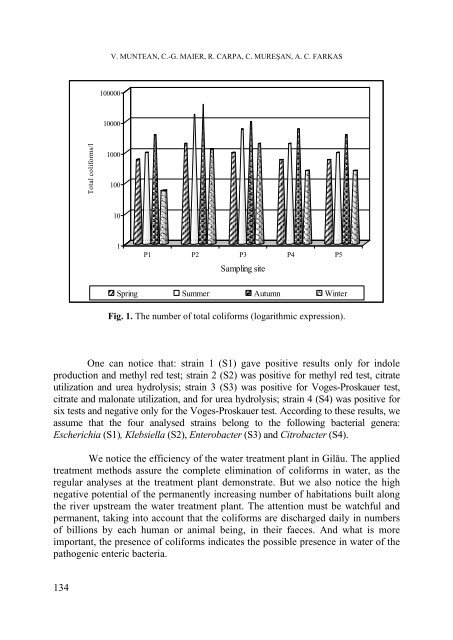
Fig. 1. The number of total coliforms (logarithmic expression).<br />
One can notice that: strain 1 (S1) gave positive results only for indole<br />
production and methyl red test; strain 2 (S2) was positive for methyl red test, citrate<br />
utilization and urea hydrolysis; strain 3 (S3) was positive for Voges-Proskauer test,<br />
citrate and malonate utilization, and for urea hydrolysis; strain 4 (S4) was positive for<br />
six tests and negative only for the Voges-Proskauer test. According to these results, we<br />
assume that the four analysed strains belong to the following bacterial genera:<br />
Escherichia (S1), Klebsiella (S2), Enterobacter (S3) and Citrobacter (S4).<br />
We notice the efficiency of the water treatment plant in Gilău. The applied<br />
treatment methods assure the complete elimination of coliforms in water, as the<br />
regular analyses at the treatment plant demonstrate. But we also notice the high<br />
negative potential of the permanently increasing number of habitations built along<br />
the river upstream the water treatment plant. The attention must be watchful and<br />
permanent, taking into account that the coliforms are discharged daily in numbers<br />
of billions by each human or animal being, in their faeces. And what is more<br />
important, the presence of coliforms indicates the possible presence in water of the<br />
pathogenic enteric bacteria.<br />
134