Samriddhi
Samriddhi
Samriddhi
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Samriddhi</strong> Project Document<br />
4.4 Approaches<br />
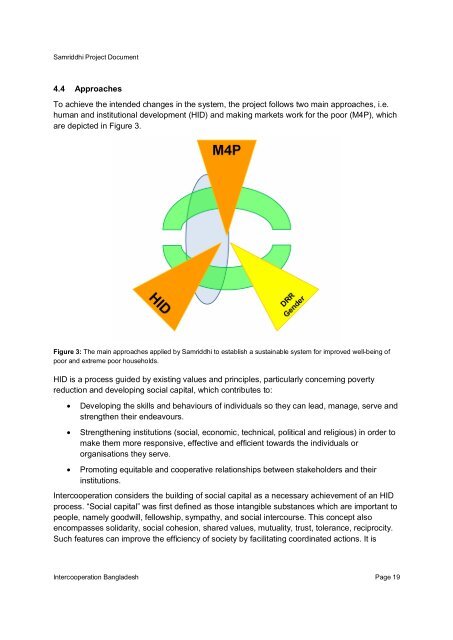
To achieve the intended changes in the system, the project follows two main approaches, i.e.<br />
human and institutional development (HID) and making markets work for the poor (M4P), which<br />
are depicted in Figure 3.<br />
Figure 3: The main approaches applied by <strong>Samriddhi</strong> to establish a sustainable system for improved well-being of<br />
poor and extreme poor households.<br />
HID is a process guided by existing values and principles, particularly concerning poverty<br />
reduction and developing social capital, which contributes to:<br />
• Developing the skills and behaviours of individuals so they can lead, manage, serve and<br />
strengthen their endeavours.<br />
• Strengthening institutions (social, economic, technical, political and religious) in order to<br />
make them more responsive, effective and efficient towards the individuals or<br />
organisations they serve.<br />
• Promoting equitable and cooperative relationships between stakeholders and their<br />
institutions.<br />
Intercooperation considers the building of social capital as a necessary achievement of an HID<br />
process. “Social capital” was first defined as those intangible substances which are important to<br />
people, namely goodwill, fellowship, sympathy, and social intercourse. This concept also<br />
encompasses solidarity, social cohesion, shared values, mutuality, trust, tolerance, reciprocity.<br />
Such features can improve the efficiency of society by facilitating coordinated actions. It is<br />
Intercooperation Bangladesh Page 19