Jahresbericht 2005 - IPHT Jena
Jahresbericht 2005 - IPHT Jena
Jahresbericht 2005 - IPHT Jena
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
42<br />
2.2.4 Photonic crystal fibres for innovative<br />
applications and devices<br />
(J. Kobelke, K. Schuster, J. Kirchhof,<br />
A. Schwuchow, K. Mörl, K. Oh)<br />
Photonic crystal fibres (PCFs) are commonly<br />
interesting as transmission media over long distances<br />
for their specific light propagation behaviour.<br />
However, the promising application potential<br />
of photonic crystal fibres also takes effect in various<br />
novel devices, e.g. PCFs with defect super<br />
lattice structure and PCF-based NxN fibre couplers.<br />
Such PCF couplers have a power stability<br />
advantage, because they can be manufactured<br />
without any dopants in the basic silica. Moreover,<br />
the transmission behaviour is mostly effected by<br />
air hole confinement light propagation, so a high<br />
numerical aperture is possible. Typical power limitations<br />
of polymer-clad fibre can be avoided by<br />
the air-clad design.<br />
We prepared special large mode area PCFs by<br />
variation of the geometric cross section design<br />
parameters. They were changed by introduction<br />
of a flexible defect in the lattice structure. The<br />
new defect design consists of the central air hole,<br />
surrounded by a holey germanium-doped silica<br />
ring. It provides a large-area annulus-mode light<br />
propagation and a chromatic dispersion with low<br />
slope ~0.05 ps/km nm 2 at 1550 nm.<br />
Fig. 2.4: Calculated dispersion curves of fundamental<br />
modes of different d core/Λ core of the super<br />
lattice PCF. Inset: fibre micrograph.<br />
PCFs with air-clad design are interesting components<br />
for optical devices. 2×2 and 4×4 multimode<br />
air-clad holey fibre couplers were prepared<br />
at the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology<br />
(GIST), South Korea, based on <strong>IPHT</strong>-manufactured<br />
PCFs. The couplers were fabricated by<br />
a novel fusion tapering technology, starting from<br />
an air-clad fibre with a core diameter of about<br />
130 µm and a very high air fraction of the holey<br />
clad ring. The couplers thus fabricated show a<br />
high port-to-port coupling uniformity over a wide<br />
spectral range from 800 nm to 1650 nm. Due to<br />
the absence of power-limiting low refractive index<br />
polymer materials to achieve the high numerical<br />
aperture, the device shows a strong potential for<br />
future high-power applications.<br />
OPTIK / OPTICS<br />
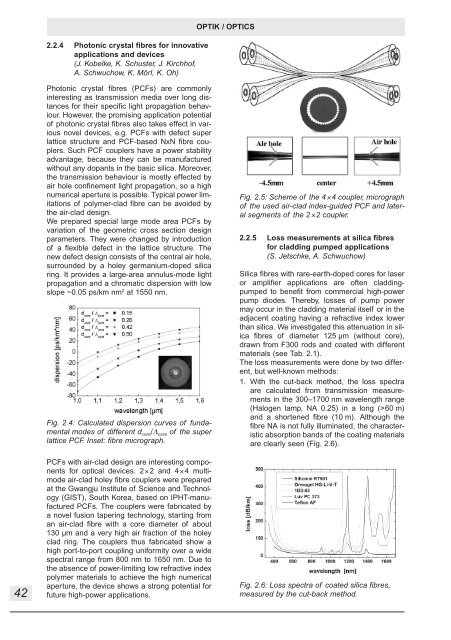
Fig. 2.5: Scheme of the 4×4 coupler, micrograph<br />
of the used air-clad index-guided PCF and lateral<br />
segments of the 2×2 coupler.<br />
2.2.5 Loss measurements at silica fibres<br />
for cladding pumped applications<br />
(S. Jetschke, A. Schwuchow)<br />
Silica fibres with rare-earth-doped cores for laser<br />
or amplifier applications are often claddingpumped<br />
to benefit from commercial high-power<br />
pump diodes. Thereby, losses of pump power<br />
may occur in the cladding material itself or in the<br />
adjacent coating having a refractive index lower<br />
than silica. We investigated this attenuation in silica<br />
fibres of diameter 125 µm (without core),<br />
drawn from F300 rods and coated with different<br />
materials (see Tab. 2.1).<br />
The loss measurements were done by two different,<br />
but well-known methods:<br />
1. With the cut-back method, the loss spectra<br />
are calculated from transmission measurements<br />
in the 300–1700 nm wavelength range<br />
(Halogen lamp, NA 0.25) in a long (>60 m)<br />
and a shortened fibre (10 m). Although the<br />
fibre NA is not fully illuminated, the characteristic<br />
absorption bands of the coating materials<br />
are clearly seen (Fig. 2.6).<br />
Fig. 2.6: Loss spectra of coated silica fibres,<br />
measured by the cut-back method.