DARPA ULTRALOG Final Report - Industrial and Manufacturing ...
DARPA ULTRALOG Final Report - Industrial and Manufacturing ...
DARPA ULTRALOG Final Report - Industrial and Manufacturing ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Proceedings of the 1st Open Cougaar Conference 7<br />
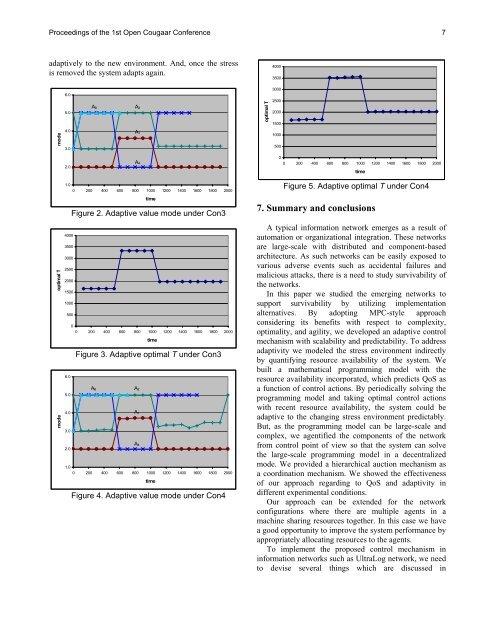
adaptively to the new environment. And, once the stress<br />
is removed the system adapts again.<br />
4000<br />
3500<br />
mode<br />
6.0<br />
5.0<br />
4.0<br />
3.0<br />
A 8 A 2<br />
A 1<br />
A 4<br />
optimal T<br />
3000<br />
2500<br />
2000<br />
1500<br />
1000<br />
500<br />
2.0<br />
0<br />
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000<br />
time<br />
mode<br />
optimal T<br />
1.0<br />
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000<br />
time<br />
Figure 2. Adaptive value mode under Con3<br />
4000<br />
3500<br />
3000<br />
2500<br />
2000<br />
1500<br />
1000<br />
500<br />
0<br />
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000<br />
time<br />
Figure 3. Adaptive optimal T under Con3<br />
A 8<br />
6.0<br />
A 2<br />
5.0<br />
4.0<br />
A 1<br />
3.0<br />
A 4<br />
2.0<br />
1.0<br />
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000<br />
time<br />
Figure 4. Adaptive value mode under Con4<br />
Figure 5. Adaptive optimal T under Con4<br />
7. Summary <strong>and</strong> conclusions<br />
A typical information network emerges as a result of<br />
automation or organizational integration. These networks<br />
are large-scale with distributed <strong>and</strong> component-based<br />
architecture. As such networks can be easily exposed to<br />
various adverse events such as accidental failures <strong>and</strong><br />
malicious attacks, there is a need to study survivability of<br />
the networks.<br />
In this paper we studied the emerging networks to<br />
support survivability by utilizing implementation<br />
alternatives. By adopting MPC-style approach<br />
considering its benefits with respect to complexity,<br />
optimality, <strong>and</strong> agility, we developed an adaptive control<br />
mechanism with scalability <strong>and</strong> predictability. To address<br />
adaptivity we modeled the stress environment indirectly<br />
by quantifying resource availability of the system. We<br />
built a mathematical programming model with the<br />
resource availability incorporated, which predicts QoS as<br />
a function of control actions. By periodically solving the<br />
programming model <strong>and</strong> taking optimal control actions<br />
with recent resource availability, the system could be<br />
adaptive to the changing stress environment predictably.<br />
But, as the programming model can be large-scale <strong>and</strong><br />
complex, we agentified the components of the network<br />
from control point of view so that the system can solve<br />
the large-scale programming model in a decentralized<br />
mode. We provided a hierarchical auction mechanism as<br />
a coordination mechanism. We showed the effectiveness<br />
of our approach regarding to QoS <strong>and</strong> adaptivity in<br />
different experimental conditions.<br />
Our approach can be extended for the network<br />
configurations where there are multiple agents in a<br />
machine sharing resources together. In this case we have<br />
a good opportunity to improve the system performance by<br />
appropriately allocating resources to the agents.<br />
To implement the proposed control mechanism in<br />
information networks such as UltraLog network, we need<br />
to devise several things which are discussed in