Annual Report 2010 (PDF, 5.2MB) - Panalpina Annual Report 2012
Annual Report 2010 (PDF, 5.2MB) - Panalpina Annual Report 2012
Annual Report 2010 (PDF, 5.2MB) - Panalpina Annual Report 2012
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Consolidated and <strong>Annual</strong> Financial Statements <strong>2010</strong><br />
based on gross profit and operating result (EBIT). Income tax expenses, finance income and costs as well as special items are not<br />
assessed by segment. Certain headquarter activities are reported as “Corporate”. These consist of corporate headquarters, including the<br />
Corporate Executive Committee, corporate communications, corporate operations, corporate human resources, corporate finance,<br />
including treasury, taxes and pension fund management.<br />
87<br />
Transfer prices between operating segments are set out at arm’s-length basis. Operating assets and liabilities consist of property, plant<br />
and equipment, goodwill and intangible assets, trade receivables / payables, other assets and liabilities such as provisions and current<br />
income taxes, which can be reasonably attributed to the reported operating segments. Non-operating assets and liabilities mainly include<br />
deferred income tax balances, post-employment benefit assets / liabilities and financial assets / liabilities such as marketable securities<br />
and investments.<br />
Foreign currency<br />
Functional currency<br />
Most Group companies use their local currency as their functional currency. Certain Group companies use other currencies (such as US<br />
dollars or euros) as their functional currency where this is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity or branch<br />
operates.<br />
Transactions and balances<br />
Local transactions in other currencies are initially reported using the exchange rate at the date of the transaction or reporting date. Gains<br />
and losses from the settlement of such transactions and gains and losses on transactions of monetary assets and liabilities denominated<br />
in other currencies are included in the income statement, except when they arise on monetary items that, in substance, form part of the<br />
Group’s net investment in a foreign entity. In such cases the gains and losses are deferred into other comprehensive income.<br />
Non-monetary items that are measured in terms of historical cost in foreign currency are translated using the exchange rate as of the dates<br />
of the initial transaction. Non-monetary items measured at fair value in a foreign currency are translated using the exchange rates on the<br />
date on which the fair value is determined.<br />
Changes in fair value of securities denominated in foreign currency classified as available-for-sale are split into components resulting from<br />
changes in the amortized cost of the security and other changes in the carrying amount of the security. Foreign exchange remeasurement<br />
differences related to changes in amortized cost are recognized in profit or loss, and other changes in the carrying amount are recognized<br />
in equity.<br />
Presentation currency<br />
Upon consolidation, assets and liabilities of Group companies using functional currency other than Swiss francs are translated into Swiss<br />
francs using a year-end rate of exchange. Income, expenses and net income and cash flows are translated at the average rates of<br />
exchange for the year. Translation differences due to the changes in exchange rates between the beginning and the end of the year and<br />
the difference between net incomes translated at the average and year-end exchange rates are recognized as a separate component<br />
of other comprehensive income.<br />
The income and expenses of foreign operations in hyperinflationary economies are translated to Swiss francs at the exchange rate on the<br />
reporting date. Prior to translating the financial statement of foreign operations in hyperinflationary economies, their financial statements<br />
are restated to account for changes in the general purchasing power of the local currency. The restatement is based on relevant price indices<br />
on the reporting date. Foreign currency differences are recognized directly in comprehensive income in the foreign currency translation<br />
reserve.<br />
On disposal of a foreign entity, the identified cumulative currency translation differences within equity relating to that foreign entity are<br />
recognized in the income statement as part of the gain or loss on divestment.<br />
Any goodwill arising on the acquisition is treated as assets and liabilities of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate.<br />
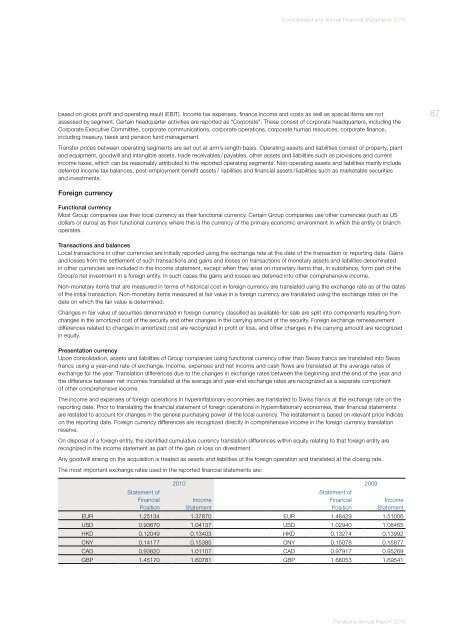
The most important exchange rates used in the reported financial statements are:<br />
Statement of<br />
Financial<br />
Position<br />
<strong>2010</strong> 2009<br />
Income<br />
Statement<br />
Statement of<br />
Financial<br />
Position<br />
Income<br />
Statement<br />
EUR 1.25134 1.37870 EUR 1.48429 1.51006<br />
USD 0.93670 1.04137 USD 1.02940 1.08465<br />
HKD 0.12049 0.13403 HKD 0.13274 0.13992<br />
CNY 0.14177 0.15385 CNY 0.15078 0.15877<br />
CAD 0.93820 1.01107 CAD 0.97917 0.95269<br />
GBP 1.45170 1.60781 GBP 1.66053 1.69541<br />
<strong>Panalpina</strong> <strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>2010</strong>