2 - Schneider Electric CZ, s.r.o.
2 - Schneider Electric CZ, s.r.o.
2 - Schneider Electric CZ, s.r.o.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Presentation<br />
Machine safety<br />
Risk assessment<br />
1<br />
Assessment of machinery related risk<br />
European legislation<br />
Machines are sources of potential risk and the Machinery Directive requires<br />
a risk assessment to ensure that any potential risk is reduced to less than<br />
the acceptable risk.<br />
2<br />
3<br />
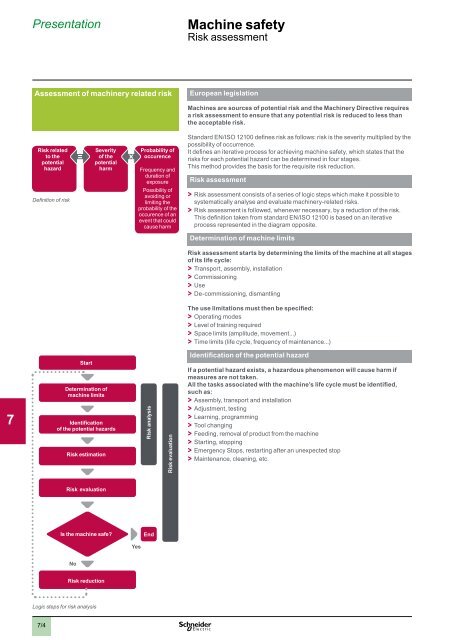
Risk related<br />
to the<br />
potential<br />
hazard<br />
Definition of risk<br />
Severity<br />
of the<br />
potential<br />
harm<br />
Probability of<br />
occurence<br />
Frequency and<br />
duration of<br />
exposure<br />
Possibility of<br />
avoiding or<br />
limiting the<br />
probability of the<br />
occurence of an<br />
event that could<br />
cause harm<br />
Standard EN/ISO 12100 defines risk as follows: risk is the severity multiplied by the<br />
possibility of occurrence.<br />
It defines an iterative process for achieving machine safety, which states that the<br />
risks for each potential hazard can be determined in four stages.<br />
This method provides the basis for the requisite risk reduction.<br />
Risk assessment<br />
> > Risk assessment consists of a series of logic steps which make it possible to<br />
systematically analyse and evaluate machinery-related risks.<br />
><br />
> Risk assessment is followed, whenever necessary, by a reduction of the risk...<br />
This definition taken from standard EN/ISO 12100 is based on an iterative<br />
process represented in the diagram opposite.<br />
Determination of machine limits<br />
4<br />
Risk assessment starts by determining the limits of the machine at all stages<br />
of its life cycle:<br />
> > Transport, assembly, installation<br />
> > Commissioning<br />
> > Use<br />
> > De-commissioning, dismantling<br />
5<br />
The use limitations must then be specified:<br />
> > Operating modes<br />
> > Level of training required<br />
> > Space limits (amplitude, movement...)<br />
> > Time limits (life cycle, frequency of maintenance...)<br />
6<br />
7<br />
8<br />
Start<br />
Determination of<br />
machine limits<br />
Identification<br />
of the potential hazards<br />
Risk estimation<br />
Risk analysis<br />
Risk evaluation<br />
Identification of the potential hazard<br />
If a potential hazard exists, a hazardous phenomenon will cause harm if<br />
measures are not taken.<br />
All the tasks associated with the machine’s life cycle must be identified,<br />
such as:<br />
> > Assembly, transport and installation<br />
> > Adjustment, testing<br />
> > Learning, programming<br />
> > Tool changing<br />
> > Feeding, removal of product from the machine<br />
> > Starting, stopping<br />
> > Emergency Stops, restarting after an unexpected stop<br />
> > Maintenance, cleaning, etc.<br />
Risk evaluation<br />
9<br />
Is the machine safe?<br />
End<br />
Yes<br />
10<br />
No<br />
Risk reduction<br />
Logic steps for risk analysis<br />
7/4