Factors Influencing Visitor's Choices of Urban Destinations in North ...
Factors Influencing Visitor's Choices of Urban Destinations in North ...
Factors Influencing Visitor's Choices of Urban Destinations in North ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
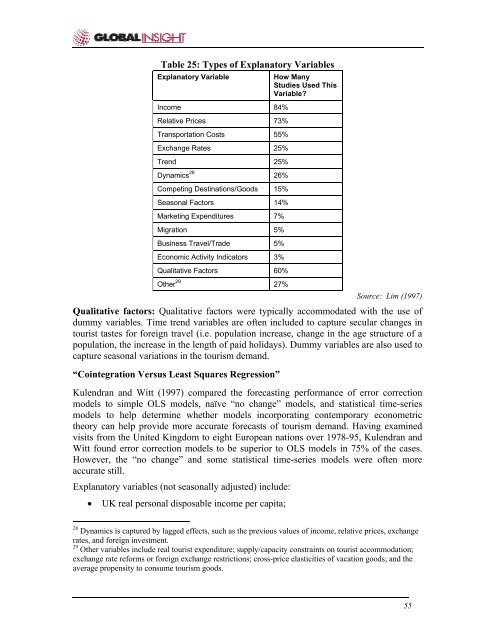
Table 25: Types <strong>of</strong> Explanatory VariablesExplanatory VariableIncome 84%Relative Prices 73%Transportation Costs 55%Exchange Rates 25%Trend 25%Dynamics 28 26%Compet<strong>in</strong>g <strong>Dest<strong>in</strong>ations</strong>/Goods 15%Seasonal <strong>Factors</strong> 14%Market<strong>in</strong>g Expenditures 7%Migration 5%Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Travel/Trade 5%Economic Activity Indicators 3%Qualitative <strong>Factors</strong> 60%Other 29 27%How ManyStudies Used ThisVariable?Source: Lim (1997)Qualitative factors: Qualitative factors were typically accommodated with the use <strong>of</strong>dummy variables. Time trend variables are <strong>of</strong>ten <strong>in</strong>cluded to capture secular changes <strong>in</strong>tourist tastes for foreign travel (i.e. population <strong>in</strong>crease, change <strong>in</strong> the age structure <strong>of</strong> apopulation, the <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> the length <strong>of</strong> paid holidays). Dummy variables are also used tocapture seasonal variations <strong>in</strong> the tourism demand.“Co<strong>in</strong>tegration Versus Least Squares Regression”Kulendran and Witt (1997) compared the forecast<strong>in</strong>g performance <strong>of</strong> error correctionmodels to simple OLS models, naïve “no change” models, and statistical time-seriesmodels to help determ<strong>in</strong>e whether models <strong>in</strong>corporat<strong>in</strong>g contemporary econometrictheory can help provide more accurate forecasts <strong>of</strong> tourism demand. Hav<strong>in</strong>g exam<strong>in</strong>edvisits from the United K<strong>in</strong>gdom to eight European nations over 1978-95, Kulendran andWitt found error correction models to be superior to OLS models <strong>in</strong> 75% <strong>of</strong> the cases.However, the “no change” and some statistical time-series models were <strong>of</strong>ten moreaccurate still.Explanatory variables (not seasonally adjusted) <strong>in</strong>clude:• UK real personal disposable <strong>in</strong>come per capita;28 Dynamics is captured by lagged effects, such as the previous values <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>come, relative prices, exchangerates, and foreign <strong>in</strong>vestment.29 Other variables <strong>in</strong>clude real tourist expenditure; supply/capacity constra<strong>in</strong>ts on tourist accommodation;exchange rate reforms or foreign exchange restrictions; cross-price elasticities <strong>of</strong> vacation goods; and theaverage propensity to consume tourism goods.55






![THIS AGREEMENT made this [date], between [name of owner] (the ...](https://img.yumpu.com/49827605/1/158x260/this-agreement-made-this-date-between-name-of-owner-the-.jpg?quality=85)








