The Ecology of Hydric Hammocks - USGS National Wetlands ...
The Ecology of Hydric Hammocks - USGS National Wetlands ...
The Ecology of Hydric Hammocks - USGS National Wetlands ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
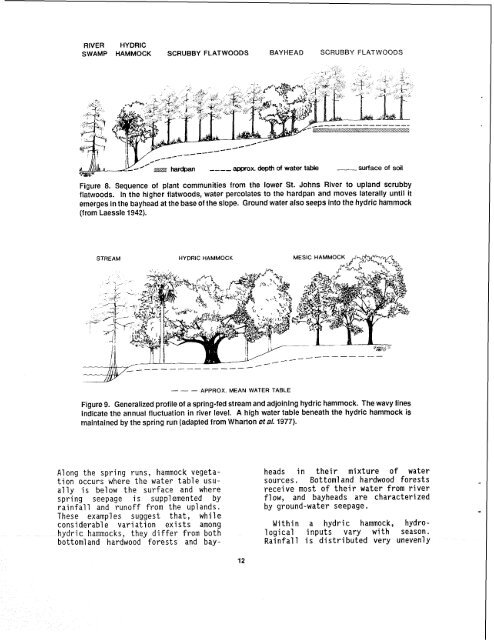
RIVER HYDRICSWAMP HAMMOCK SCRUBBY FLATWOODS BAYWEAD SCRUBBY FLATWOODSwater taMI_ surface <strong>of</strong> soilFigure 8. Sequence <strong>of</strong> plant communities from the lower St. Johns River to upland scrubbyflatwoods. In the higher flatwoods, water percolates to the hardpan and moves laterally until itemerges in the bayhead at the base <strong>of</strong> the slope. Ground water also seeps into the hydric hammock(from Laessle 1942).STREAM HYDRIC HAMMOCK MESlC HAMM--- APPROX MEAN WATER TABLEFigure 9. Generalized pr<strong>of</strong>ile <strong>of</strong> a spring-fed stream and adjoining hydric hammock. <strong>The</strong> wavy linesindicate the annual fluctuation in river level. A high water table beneath the hydric hammock ismaintained by the spring run (adapted from Wharton et al. 1977).A1 ong the spring runs, hammock vegetationoccurs where the water table usuallyis below the surface and wherespring seepage is supplemented byrainfall and run<strong>of</strong>f from the uplands.<strong>The</strong>se examples suggest that, whileconsiderable variation exists amonghydric hammocks, they differ from bothbottomland hardwood forests and bay-heads in their mixture <strong>of</strong> watersources. Bottom1 and hardwood forestsreceive most <strong>of</strong> their water from riverflow, and bayheads are characterizedby ground-water seepage..Within a hydric hammock, hydrologicalinputs vary with season.Rainfall is distributed very unevenly