CUVX Design Report - the AOE home page - Virginia Tech
CUVX Design Report - the AOE home page - Virginia Tech
CUVX Design Report - the AOE home page - Virginia Tech
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
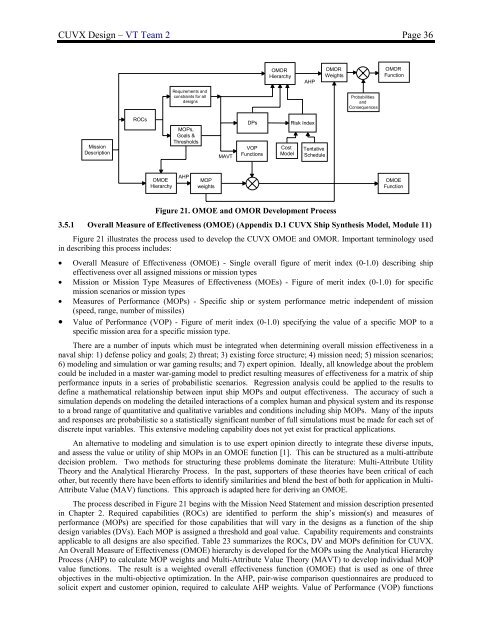
<strong>CUVX</strong> <strong>Design</strong> – VT Team 2 Page 36OMORHierarchyAHPOMORWeightsOMORFunctionRequirements andconstraints for alldesignsProbabilitiesandConsequencesMissionDescriptionROCsMOPs,Goals &ThresholdsMAVTDPsVOPFunctionsCostModelRisk IndexTentativeScheduleOMOEHierarchyAHPMOPweightsOMOEFunctionFigure 21. OMOE and OMOR Development Process3.5.1 Overall Measure of Effectiveness (OMOE) (Appendix D.1 <strong>CUVX</strong> Ship Syn<strong>the</strong>sis Model, Module 11)Figure 21 illustrates <strong>the</strong> process used to develop <strong>the</strong> <strong>CUVX</strong> OMOE and OMOR. Important terminology usedin describing this process includes:• Overall Measure of Effectiveness (OMOE) - Single overall figure of merit index (0-1.0) describing shipeffectiveness over all assigned missions or mission types• Mission or Mission Type Measures of Effectiveness (MOEs) - Figure of merit index (0-1.0) for specificmission scenarios or mission types• Measures of Performance (MOPs) - Specific ship or system performance metric independent of mission(speed, range, number of missiles)• Value of Performance (VOP) - Figure of merit index (0-1.0) specifying <strong>the</strong> value of a specific MOP to aspecific mission area for a specific mission type.There are a number of inputs which must be integrated when determining overall mission effectiveness in anaval ship: 1) defense policy and goals; 2) threat; 3) existing force structure; 4) mission need; 5) mission scenarios;6) modeling and simulation or war gaming results; and 7) expert opinion. Ideally, all knowledge about <strong>the</strong> problemcould be included in a master war-gaming model to predict resulting measures of effectiveness for a matrix of shipperformance inputs in a series of probabilistic scenarios. Regression analysis could be applied to <strong>the</strong> results todefine a ma<strong>the</strong>matical relationship between input ship MOPs and output effectiveness. The accuracy of such asimulation depends on modeling <strong>the</strong> detailed interactions of a complex human and physical system and its responseto a broad range of quantitative and qualitative variables and conditions including ship MOPs. Many of <strong>the</strong> inputsand responses are probabilistic so a statistically significant number of full simulations must be made for each set ofdiscrete input variables. This extensive modeling capability does not yet exist for practical applications.An alternative to modeling and simulation is to use expert opinion directly to integrate <strong>the</strong>se diverse inputs,and assess <strong>the</strong> value or utility of ship MOPs in an OMOE function [1]. This can be structured as a multi-attributedecision problem. Two methods for structuring <strong>the</strong>se problems dominate <strong>the</strong> literature: Multi-Attribute UtilityTheory and <strong>the</strong> Analytical Hierarchy Process. In <strong>the</strong> past, supporters of <strong>the</strong>se <strong>the</strong>ories have been critical of eacho<strong>the</strong>r, but recently <strong>the</strong>re have been efforts to identify similarities and blend <strong>the</strong> best of both for application in Multi-Attribute Value (MAV) functions. This approach is adapted here for deriving an OMOE.The process described in Figure 21 begins with <strong>the</strong> Mission Need Statement and mission description presentedin Chapter 2. Required capabilities (ROCs) are identified to perform <strong>the</strong> ship’s mission(s) and measures ofperformance (MOPs) are specified for those capabilities that will vary in <strong>the</strong> designs as a function of <strong>the</strong> shipdesign variables (DVs). Each MOP is assigned a threshold and goal value. Capability requirements and constraintsapplicable to all designs are also specified. Table 23 summarizes <strong>the</strong> ROCs, DV and MOPs definition for <strong>CUVX</strong>.An Overall Measure of Effectiveness (OMOE) hierarchy is developed for <strong>the</strong> MOPs using <strong>the</strong> Analytical HierarchyProcess (AHP) to calculate MOP weights and Multi-Attribute Value Theory (MAVT) to develop individual MOPvalue functions. The result is a weighted overall effectiveness function (OMOE) that is used as one of threeobjectives in <strong>the</strong> multi-objective optimization. In <strong>the</strong> AHP, pair-wise comparison questionnaires are produced tosolicit expert and customer opinion, required to calculate AHP weights. Value of Performance (VOP) functions