Design, Fabrication and Characterization of a Microwave Resonator ...
Design, Fabrication and Characterization of a Microwave Resonator ...
Design, Fabrication and Characterization of a Microwave Resonator ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
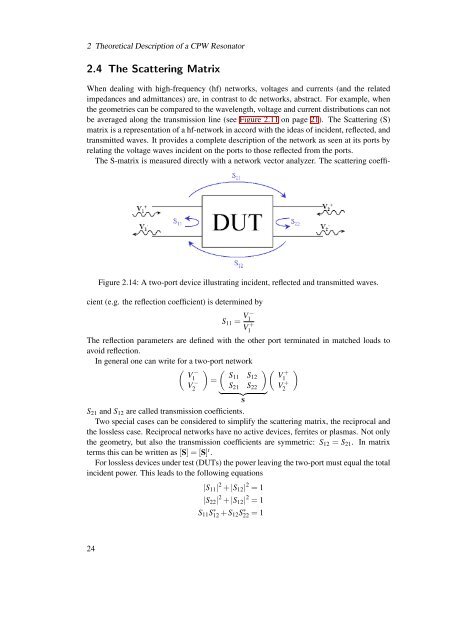
2 Theoretical Description <strong>of</strong> a CPW <strong>Resonator</strong>2.4 The Scattering MatrixWhen dealing with high-frequency (hf) networks, voltages <strong>and</strong> currents (<strong>and</strong> the relatedimpedances <strong>and</strong> admittances) are, in contrast to dc networks, abstract. For example, whenthe geometries can be compared to the wavelength, voltage <strong>and</strong> current distributions can notbe averaged along the transmission line (see Figure 2.11 on page 21). The Scattering (S)matrix is a representation <strong>of</strong> a hf-network in accord with the ideas <strong>of</strong> incident, reflected, <strong>and</strong>transmitted waves. It provides a complete description <strong>of</strong> the network as seen at its ports byrelating the voltage waves incident on the ports to those reflected from the ports.The S-matrix is measured directly with a network vector analyzer. The scattering coeffi-Figure 2.14: A two-port device illustrating incident, reflected <strong>and</strong> transmitted waves.cient (e.g. the reflection coefficient) is determined byS 11 = V 1−V1+The reflection parameters are defined with the other port terminated in matched loads toavoid reflection.In general one can write for a two-port network( ) ( )( )V−1S11 SV2− =12 V+1S 21 S 22 V2+ } {{ }SS 21 <strong>and</strong> S 12 are called transmission coefficients.Two special cases can be considered to simplify the scattering matrix, the reciprocal <strong>and</strong>the lossless case. Reciprocal networks have no active devices, ferrites or plasmas. Not onlythe geometry, but also the transmission coefficients are symmetric: S 12 = S 21 . In matrixterms this can be written as [S] = [S] t .For lossless devices under test (DUTs) the power leaving the two-port must equal the totalincident power. This leads to the following equations|S 11 | 2 + |S 12 | 2 = 1|S 22 | 2 + |S 12 | 2 = 1S 11 S ∗ 12 + S 12 S ∗ 22 = 124