Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
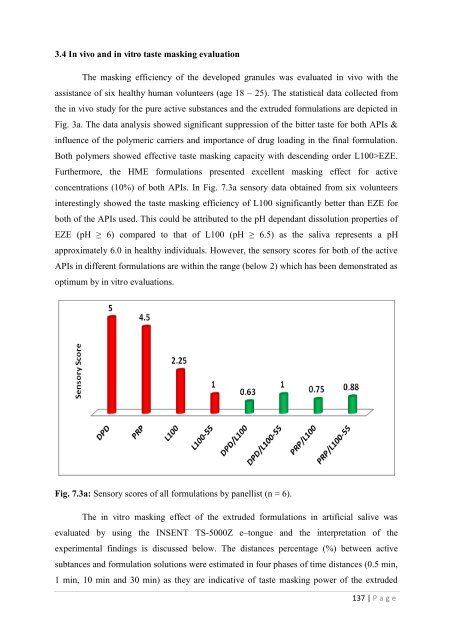
3.4 In vivo and in vitro t<strong>as</strong>te m<strong>as</strong>king evaluationThe m<strong>as</strong>king efficiency <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> developed granules w<strong>as</strong> evaluated in vivo with <strong>the</strong><strong>as</strong>sistance <strong>of</strong> six healthy human volunteers (age 18 – 25). The statistical data collected from<strong>the</strong> in vivo study <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> pure active substances and <strong>the</strong> extruded <strong>for</strong>mulations are depicted inFig. 3a. The data analysis showed significant suppression <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> bitter t<strong>as</strong>te <strong>for</strong> both APIs &influence <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> polymeric carriers and importance <strong>of</strong> drug loading in <strong>the</strong> final <strong>for</strong>mulation.Both polymers showed effective t<strong>as</strong>te m<strong>as</strong>king capacity with descending order L100>EZE.Fur<strong>the</strong>rmore, <strong>the</strong> HME <strong>for</strong>mulations presented excellent m<strong>as</strong>king effect <strong>for</strong> activeconcentrations (10%) <strong>of</strong> both APIs. In Fig. 7.3a sensory data obtained from six volunteersinterestingly showed <strong>the</strong> t<strong>as</strong>te m<strong>as</strong>king efficiency <strong>of</strong> L100 significantly better than EZE <strong>for</strong>both <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> APIs used. This could be attributed to <strong>the</strong> pH dependant dissolution properties <strong>of</strong>EZE (pH ≥ 6) compared to that <strong>of</strong> L100 (pH ≥ 6.5) <strong>as</strong> <strong>the</strong> saliva represents a pHapproximately 6.0 in healthy individuals. However, <strong>the</strong> sensory scores <strong>for</strong> both <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> activeAPIs in different <strong>for</strong>mulations are within <strong>the</strong> range (below 2) which h<strong>as</strong> been demonstrated <strong>as</strong>optimum by in vitro evaluations.Fig. 7.3a: Sensory scores <strong>of</strong> all <strong>for</strong>mulations by panellist (n = 6).The in vitro m<strong>as</strong>king effect <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> extruded <strong>for</strong>mulations in artificial salive w<strong>as</strong>evaluated by using <strong>the</strong> INSENT TS-5000Z e–tongue and <strong>the</strong> interpretation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>experimental findings is discussed below. The distances percentage (%) between activesubtances and <strong>for</strong>mulation solutions were estimated in four ph<strong>as</strong>es <strong>of</strong> time distances (0.5 min,1 min, 10 min and 30 min) <strong>as</strong> <strong>the</strong>y are indicative <strong>of</strong> t<strong>as</strong>te m<strong>as</strong>king power <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> extruded137 | P a g e